The World’s Largest AI Agricultural Robot
Category: AI Insights
Published date: 16.09.2020
Read time: 5 min
As world leaders struggle to control the effects of global climate change, researchers are already working on identifying how farmers will grow the crops of the future as the Earth’s temperature increases. In order to help them better understand the effects of climate change and be better prepared for what lies ahead, scientists have developed the Field Scanalyzer, an AI-powered robot that is the largest of its kind. Let’s take a closer look at this innovative project and how it will impact the future of agriculture.
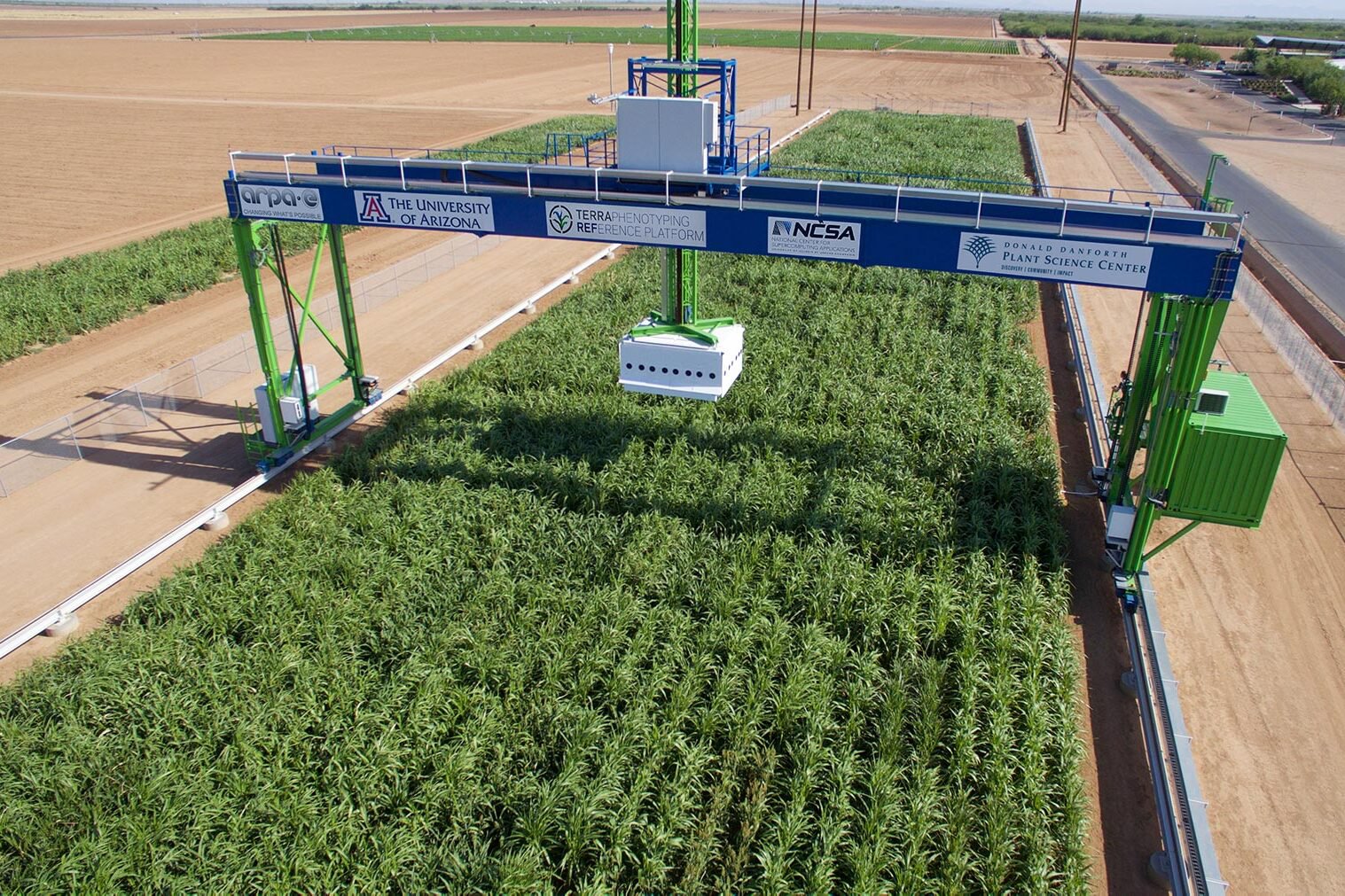

About the Field Scanalyzer
The Field Scanalyzer robot stands 70 feet tall, 92 feet wide, and weighs 30 tonnes, making it the largest agricultural robot in the world. Visually, it resembles an oversized scaffold with a box perched in its middle as it uses rails to hover over two acres of land taking pictures of corn, lettuce, wheat, and many other crops. This is part of a broad project funded by the US Department of Energy and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation that aims to help scientists and farmers produce stress-resilient crops, ones that could grow in warmer and drier climates and could help produce biofuels to reduce reliance on foil fuels.
The project is located in Maricopa, Arizona since this place has what researchers consider to be “the climate of tomorrow, today”. Since research has shown that the Earth’s surface temperature increases at an average rate of 0.18°C / 0.32°F per decade so in a hundred years the Earth’s temperature will be a lot hotter than what it is right now and we need to start preparing for all of the possible changes today. Therefore, the long-term goals of the project are to understand how we are going to address this problem and gain deeper insights into drought resiliency.
How Does the Field Scanalyzer Work?
The Field Scanalyzer is built on rails that allow it to travel back and forth while taking pictures of each plant with a computer vision camera. It takes 100 images of each plant in a few seconds which translates to 10 terabytes of data each day. To put this into perspective, this is equivalent to about 2.6 million copies of Tolstoy’s War and Peace. All of the data is sent to servers located in Illinois and Missouri and, later on, this data is used by researchers at George Washington University and St. Louis University to teach the machine learning algorithms to spot connections between particular genes and the plant traits that have been observed by the robot.
Such research requires extensive data annotation work as well since the robot needs to be able to identify whether the observed organism is a crop and needs to be there as opposed to something like a weed or a bug. Also, all of the images need to be labeled with specific characteristics and qualities that identify the crop as being resilient to drought. Such work would require not only labeling but semantic segmentation since the height, width, and length all need to be exactly right in order to get accurate results. This work can be very time-consuming which is why a lot of companies choose to outsource it to a service provider since it allows researchers to focus on their core tasks.
Gaining Transformative Insights
The Field Scanalyzer can provide game-changing insights into the variety of plants that are the most efficient with sunlight. Which plants are the best at taking that natural energy and transforming it into biomass and with the least amount of water possible? Scientists are hoping that the insights they gain from the project will be transferable to other dry locations and help further drive sustainable farming and production of nutritious calories for people and improving the human condition. Machine learning allows researchers to stitch together all of the images from the robot and study the progress of each plant individually and produce predictive models for how each plant will perform in particular scenarios.
Mindy Support is Supporting Researchers Develop AI Projects
Mindy Support takes the burden of data annotation off the shoulders of researchers allowed to focus solely on their project. We have extensive experience actualizing data annotation projects in the agriculture, automotive, healthcare and many other industries We are one of the largest BPO providers in Eastern Europe with more than 2,000 employees in six locations all over Ukraine. We can source and recruit candidates quickly and the QA processes we have in place allow us to scale your project without sacrificing the quality.