AI Robots are Powering the Farmtech Revolution
Category: AI Insights
Published date: 30.11.2020
Read time: 6 min
Automation has been picking up steam in the agriculture sector even before the COVID-19 crisis hit, but, nowadays, it is becoming something farmers cannot live without. The ongoing health risks are generating even more demand on top of labor shortages as farmers are having a difficult time finding even seasonal work during this difficult time. Let’s explore these issues in greater detail in order to understand why AI-powered robots are in such high demand and why it could be a viable alternative to human labor.
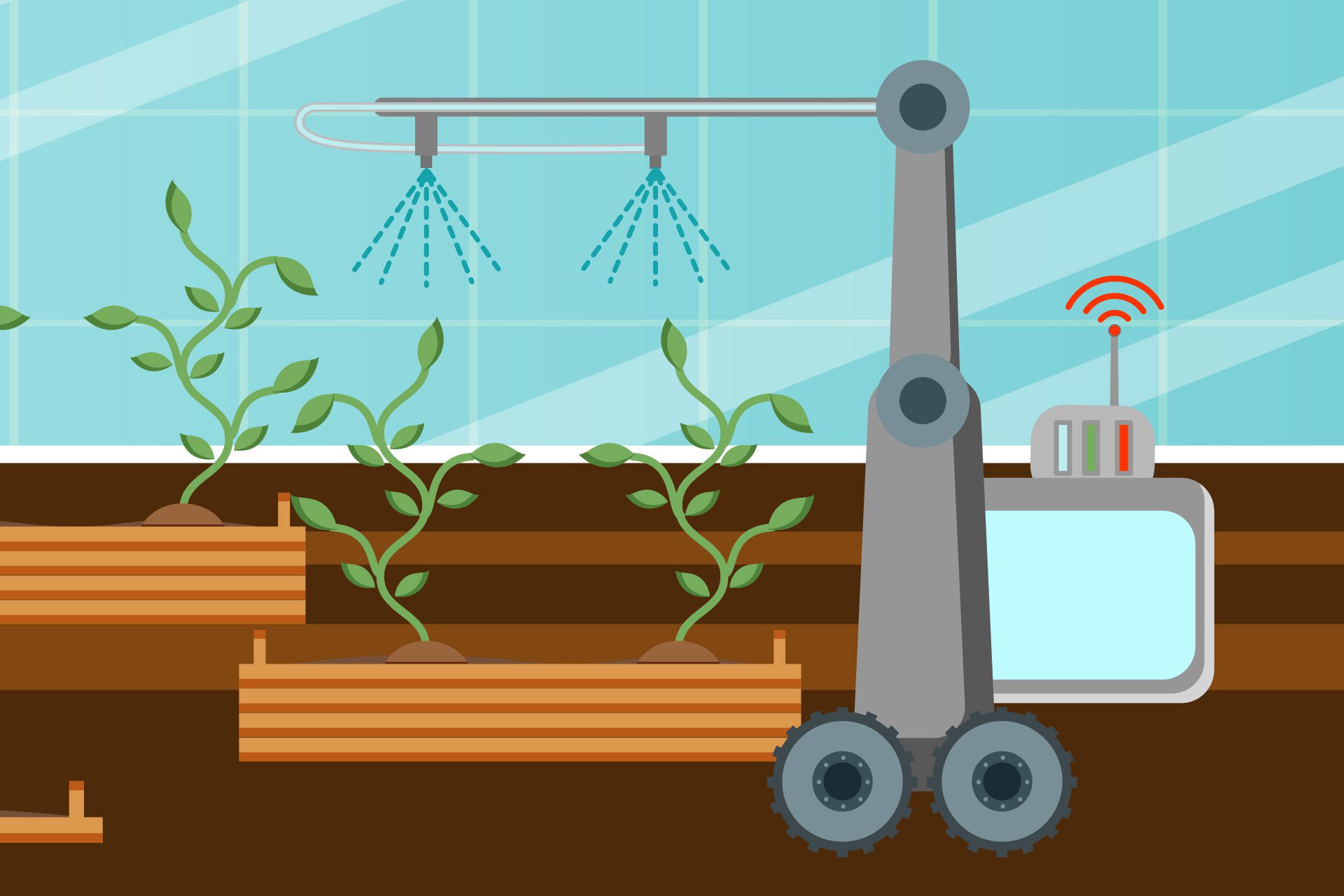

Agriculture is Already Heavily Automated
Farmers in the US depend on automation to fill labor shortages since it is very difficult to find people willing to do this type of work and it is very expensive to hire seasonal workers from outside the country on H2A visas. The COVID-19 crisis is making matters worse since a lot of embassies and government agencies are not able to work at full capacity, which is causing delays in issuing visas. The problem of finding workers willing to do the difficult job of harvesting is also something the UK government is dealing with as well. On top of all this, we have an ongoing health crisis where farmers also cannot operate in full capacity in fear of spreading the virus.
Automation has already been playing an important role in the agriculture industry as the entire sector shrank to less than 2% of the labor force in the US. Crops like potatoes, wheat, and corn are usually harvested by machines, but there is still the issue of picking more delicate fruits and vegetables. Thanks to the latest developments in AI like computer vision and complex motion planning, robots are able to handle such tasks as well.
Practical Applications of AI Robots
One of the interesting new products in harvesting delicate crops is a robot called Virgo, created by RootAI. This is a tomato-picking robot that is currently in the R&D stages but is expected to be widely available in the US next year. There are many different challenges this robot needs to overcome in order to perform its job correctly. First of all, it needs to physically travel to the needed tomato row, then it needs to identify the ripe tomatoes, and, finally, it needs to pick them without squishing them. Each of these aspects is powered by AI. LiDAR technology allows the robot to see the world around them and navigate their way to the needed location. Computer vision allows the robot to determine whether or not a particular tomato is ripe for harvesting. Finally, motion planning and object manipulation allow the robot to plan and adjust its grip on the tomato without squishing it.
Both LiDAR and computer vision require a lot of data annotation work to be performed since there are so many details the robot must be able to understand. LiDAR creates a 3D point cloud which is a representation of how the robot sees the physical world. Human data annotators would need to label all of the objects in the 3D point cloud so the robot can identify them independently in the future. Computer vision would require more detailed data annotation work to be done, such as semantic segmentation, since the difference between ripe tomatoes and almost-ripe tomatoes is not all that big. This means the robots would need to be able to identify all of the shades of red on the tomato to determine whether a particular tomato should be harvested.
Are Such Robots Economically Viable?
Even though creating the types of AI robots described above is difficult enough, companies need to make sure that they make financial sense for farmers to buy them. Since it is quite costly to hire top-quality developers and perform all of the needed research and development, the cost of these robots might be simply unaffordable to farmers. However, companies developing such robots believe that such robots are economically viable since the costs of creating a robot have decreased over the years. Research from Ark Invest backs this up since their research determined that the cost of creating a robot will decrease by 65% to levels much lower than most analysts now anticipate, by 2025.
Mindy Support is Helping Companies Develop New AI Agricultural Products
Thanks to the comprehensive data annotation services provided by Mindy Support, companies can further reduce development costs by hiring dedicated data annotation teams in Ukraine. We are one of the largest BPO companies in Eastern Europe with more than 2,000 employees in six locations all over Ukraine. Thanks to our size and location, we are able to source and recruit the needed number of candidates quickly and we can scale your team without sacrificing the quality of the annotation work. Our long track record of success makes us a reliable partner to actualize your data annotation project.