AI-Powered Construction Vehicles are Making Sites Safer and More Efficient
Category: AI Insights
Published date: 03.04.2023
Read time: 6 min
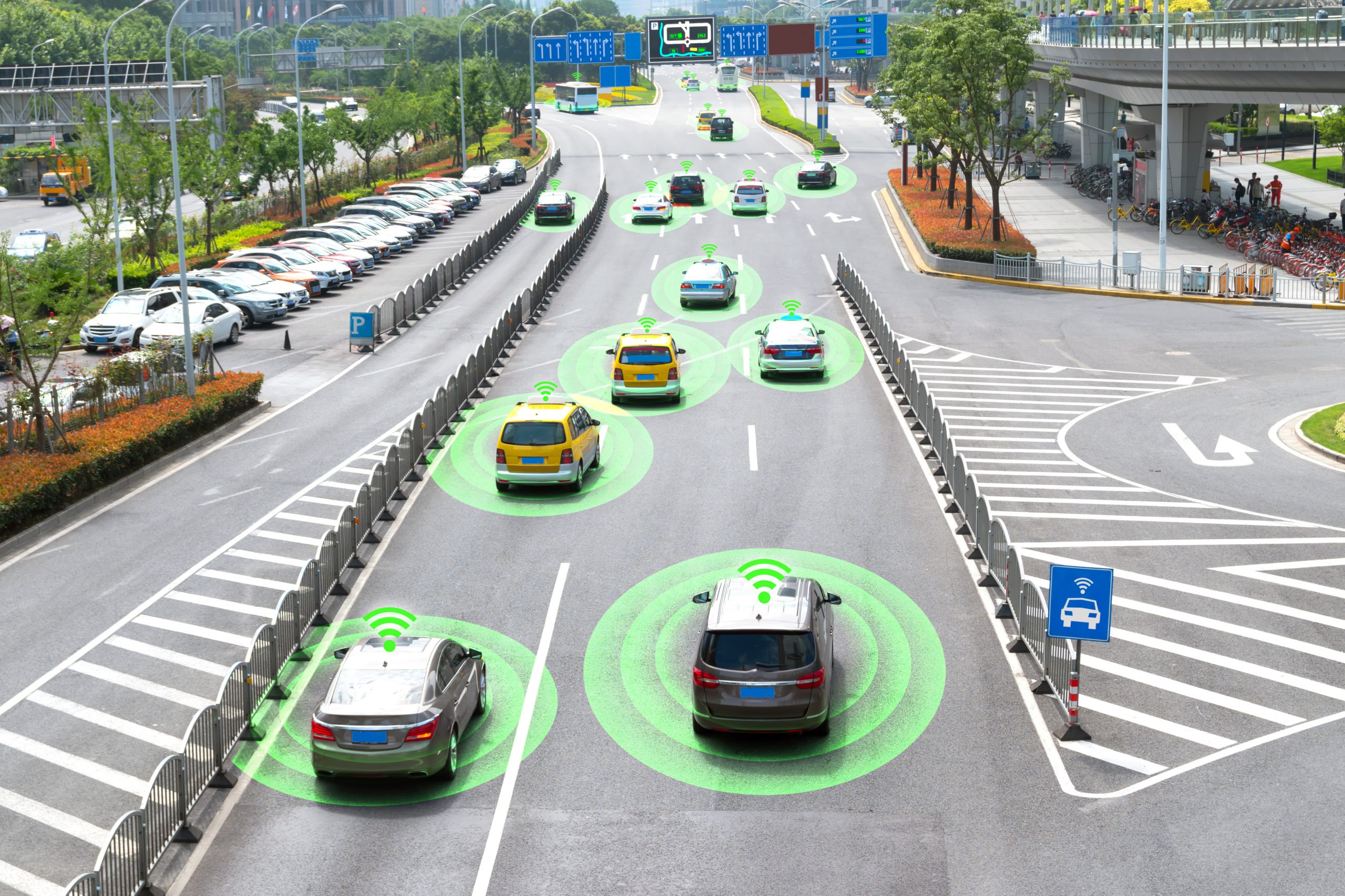
While self-driving cars get the majority of attention from the media and consumers, a lot of developments are being made in autonomous heavy machinery on construction sites. These new advances are making it easier for project managers and construction workers to get their work done faster and keep the project on schedule. In this article, we will take a look at some of the self-driving construction equipment that is already being used and the data annotation required to train the AI to make them a reality.
Self-Operating Bulldozers
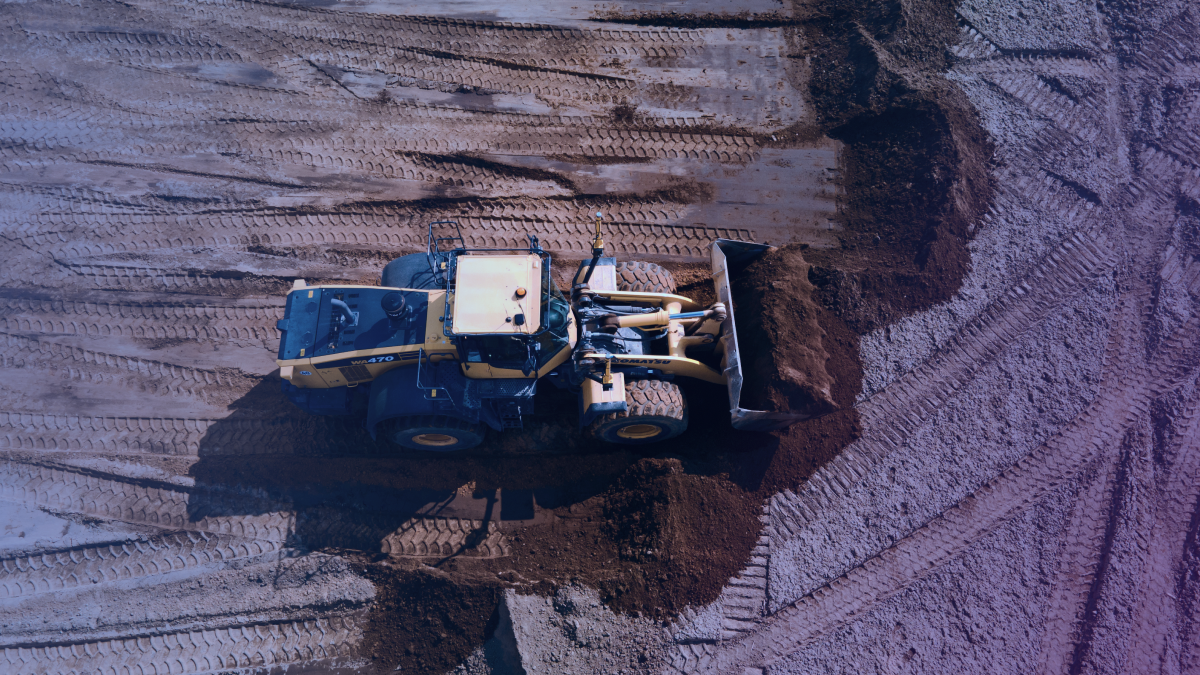

Currently, autonomous bulldozers are being developed to perform repetitive tasks like dewatering, planting, and heap leaching. It would also help avoid exposure to potentially dangerous operating scenarios and even pollution. This is a win-win for both construction companies and workers because, for the company, this means less operational costs since machines can perform this low-level work. This also frees up workers to perform more important work, thereby increasing efficiency and productivity.
Also, construction workers can enjoy a higher level of safety because this could help avoid exposure to potentially dangerous operating scenarios and even pollution. We also need to keep in mind that driving something that’s off-road leads to faster neck, arm, and hand fatigue, which also could lead to possible hazardous scenarios.
Autonomous Excavators
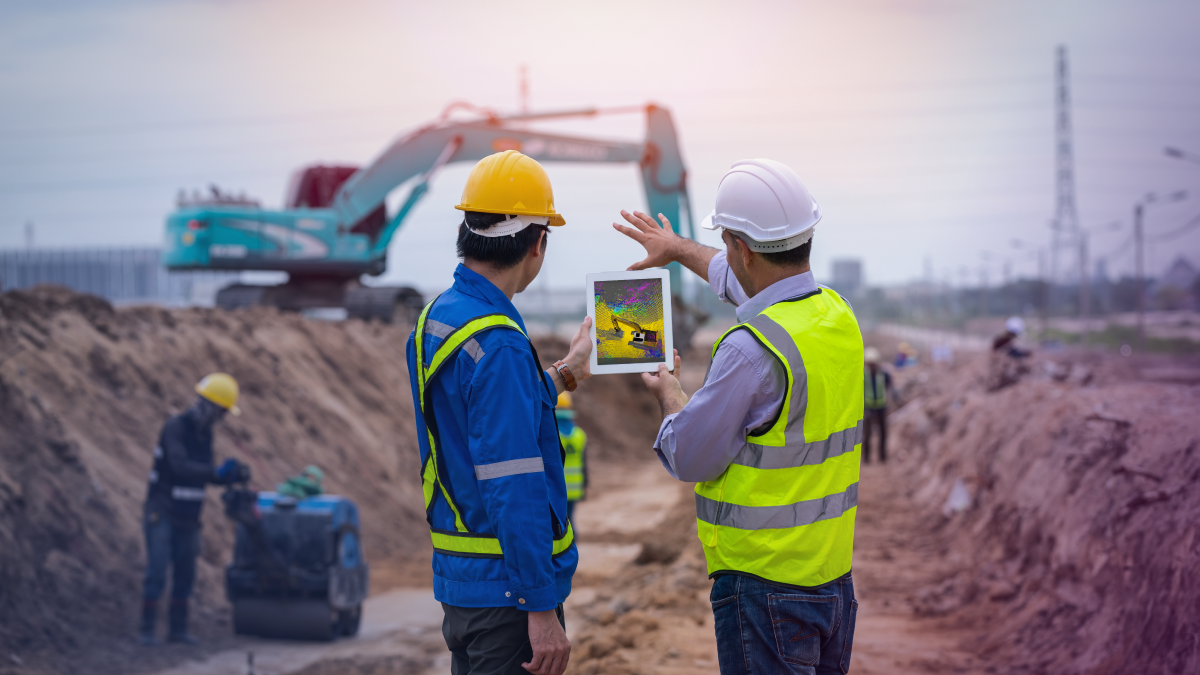

On building sites, autonomous excavators automate the excavation process using cutting-edge robotic technology. Autonomous excavators can monitor how much dirt they are moving in real-time by using sensors to gather data on the area around them. Limiting the movement of extra soil helps to make building sites more effective and environmentally sustainable.
These autonomous excavators are really useful for digging trenches. This is a very repetitive process but requires a lot of accuracy because you need to make sure that you are digging at the right depth. If you go too deep, you risk destabilizing the trench walls, and then it’s not safe for the people helping to install the pipelines or cables. In addition to digging trenches, these autonomous excavators can be used for material handling applications in unstructured environments, including mining and construction. Operating excavators in a real-world environment can be challenging due to extreme conditions such as rock sliding, ground collapse, or excessive dust—and can result in fatalities and injuries.
Driverless Hauling Trucks
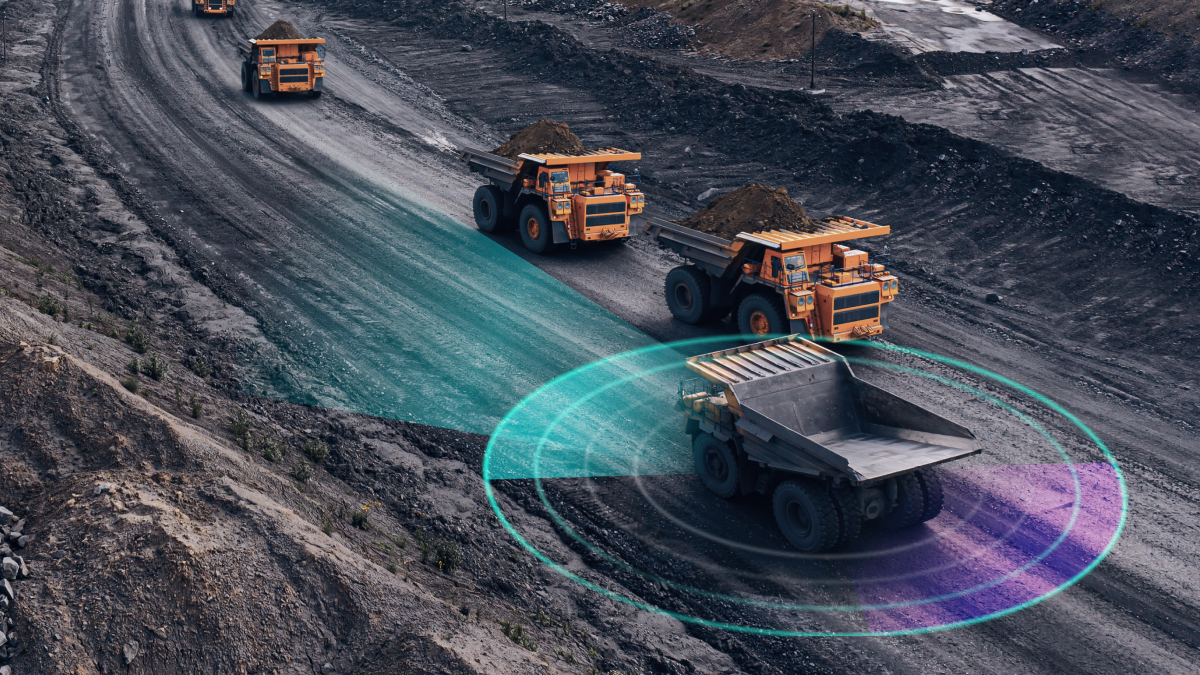

These types of trucks are great for projects where any type of excavation or mining is being performed. Transport vehicles take predictable paths and move at predictable rates. They move back and forth from one fixed spot to another, typically from a loading tool to a dump and back. Additionally, autonomous machines are not affected by the distractions and exhaustion that result from long periods of monotonous work at the wheel for human operators. AI-powered driverless hauling trucks reduce vulnerability to the risk of equipment contact with auxiliary equipment or equipped manual vehicles (EMV). Inside the truck, all data obtained is compiled so that the software can make a suitable decision. Calculating the maximum speed allowed to a nearby equipment or estimated time for a truck to break are possible decisions.
What Types of Data Annotation are Needed to Train These AI Technologies?
The autonomous technologies we looked at rely on LiDAR and computer vision cameras to navigate their surroundings. Let’s take a look at LiDAR first. The way LiDAR works is that it sends out pulses of light that bounce off objects and return back to the LiDAR. The longer it takes the light to bounce off and return, the farther away the object is located. This creates a 3D Point Cloud, which needs to be annotated with methods ranging from tagging to more detailed types of annotation, like semantic segmentation.
Computer vision cameras need to be trained with methods like 2D/3D bounding boxes, although objects that do not neatly fit into rectangular boxes will need to be annotated with polygons. Semantic segmentation will also be necessary since it delineates boundaries between similar objects and labels them under the same identification. However, Instance segmentation can also be used here because it tracks and counts the presence, location, count, size, and shape of objects in an image.
Trust Mindy Support With All of Your Data Annotation Needs
Mindy Support is a global provider of data annotation services and is trusted by Fortune 500 and GAFAM companies. With more than ten years of experience under our belt and offices and representatives in Cyprus, Poland, Romania, Bulgaria, India, OAE, and Ukraine, Mindy Support’s team now stands strong with 2000+ professionals helping companies with their most advanced data annotation challenges.