The Role of Data Annotation in Constructing Autonomous Vehicles
Data annotation is essential for the advancement and enhancement of autonomous vehicles, acting as the fundamental building block for the machine learning algorithms driving their decision-making capabilities. In this context, data annotation involves the meticulous labeling of various elements within sensor data, such as images, LiDAR scans, and radar signals, to provide crucial context for training algorithms.
Annotations typically include identifying objects such as pedestrians, vehicles, and traffic signs, as well as delineating lanes and other relevant features of the environment. High-quality annotations enable autonomous vehicles to accurately perceive and interpret their surroundings, facilitating the development of robust models capable of navigating complex real-world scenarios with precision and safety. In this article we will take a look at the role of data annotation in developing autonomous vehicles.
What Data Is Used for Autonomous Vehicles
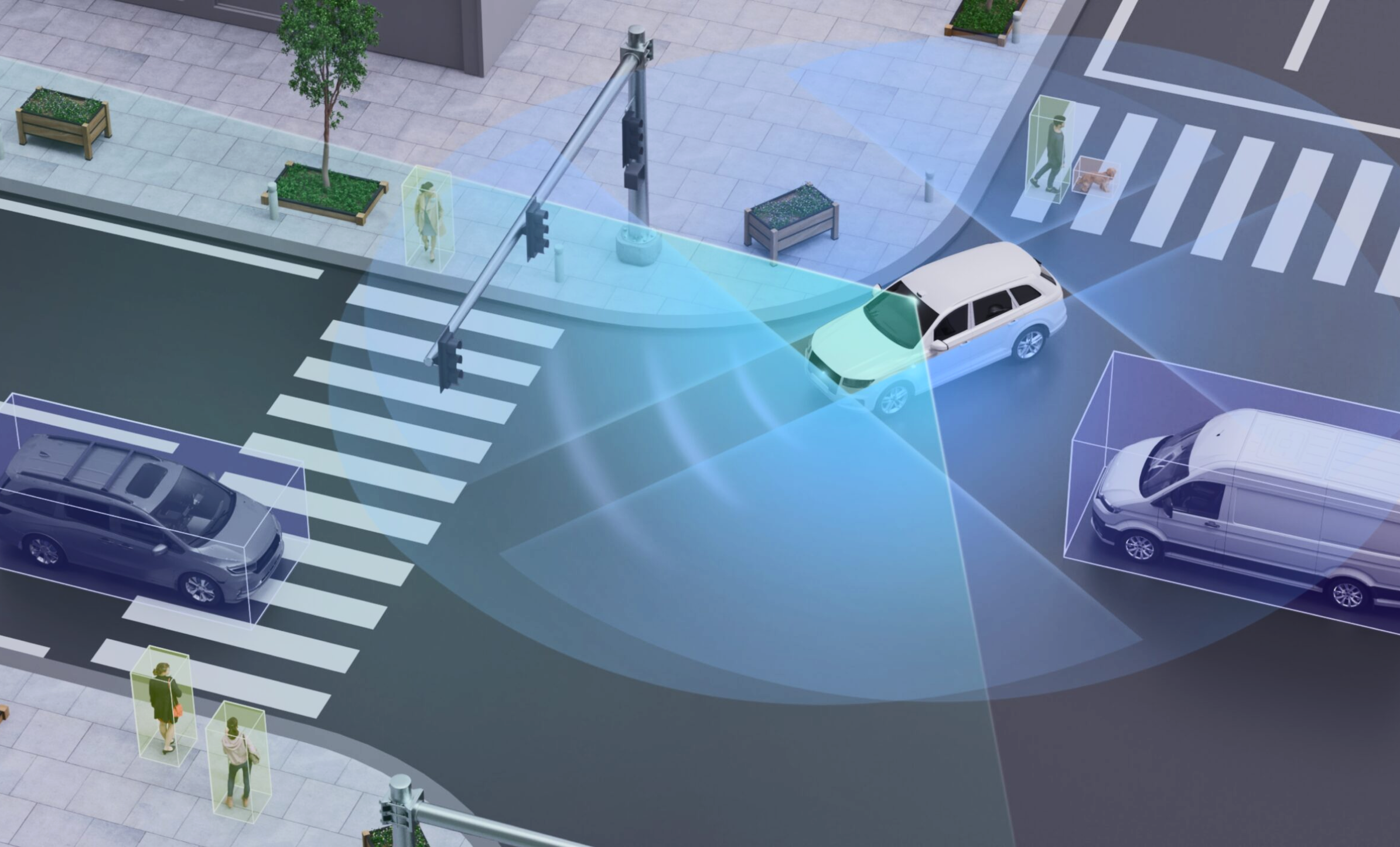
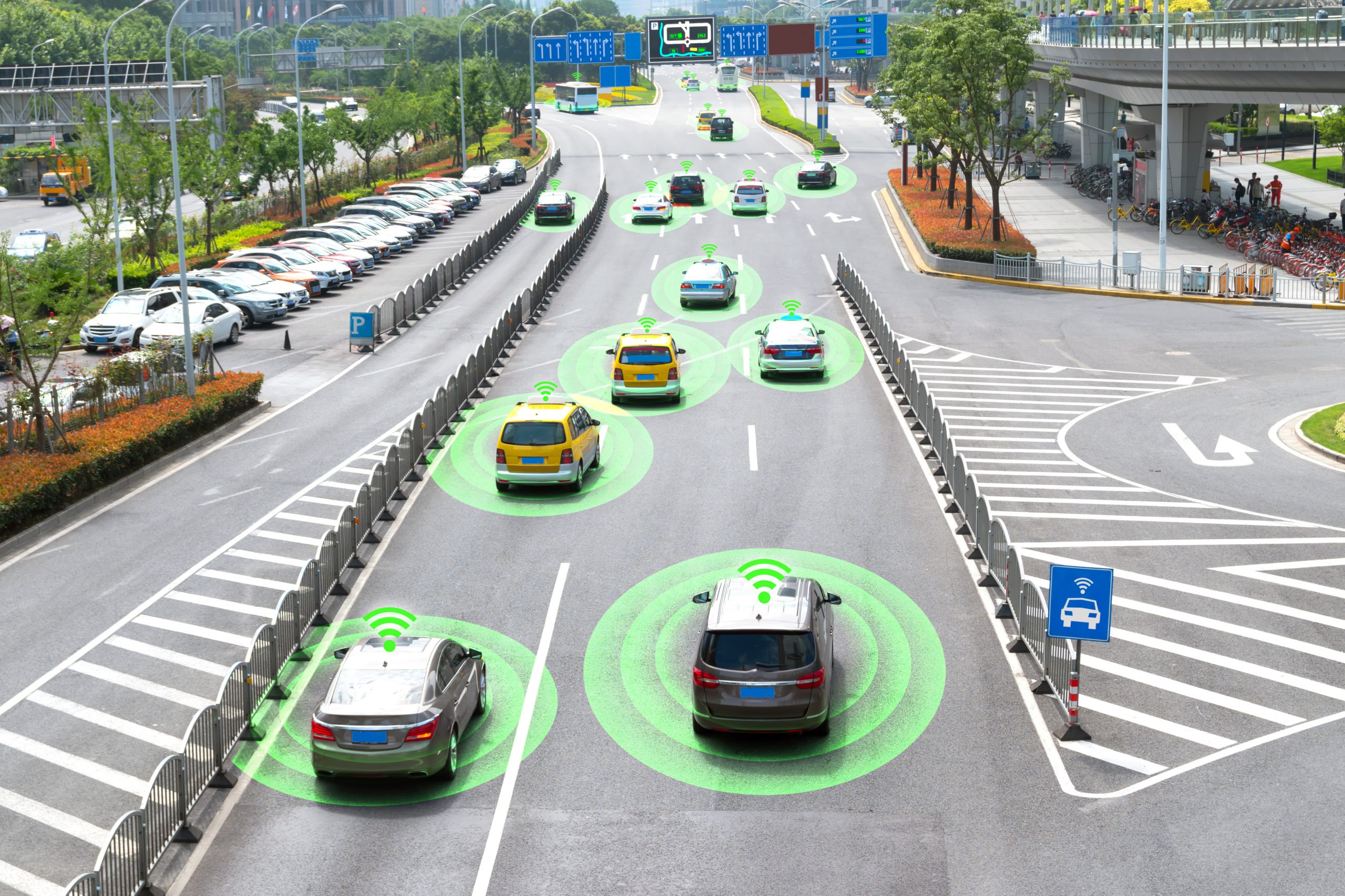
Data plays a fundamental role in the development of autonomous vehicles, serving as the bedrock upon which their intelligence is built. Throughout the developmental life cycle, vast amounts of data are collected from various sensors, including cameras, LIDAR, radar, and GPS, capturing rich information about the vehicle’s surroundings and its interactions with the environment. This raw data is then meticulously annotated and curated to provide context and labels necessary for training sophisticated machine learning algorithms.
Through extensive data processing and analysis, autonomous vehicles learn to recognize and interpret objects, understand road signs, predict pedestrian movements, and navigate complex traffic scenarios. Additionally, data from real-world driving experiences are continuously fed back into the system, enabling iterative improvements and fine-tuning of algorithms to enhance performance, safety, and adaptability. Ultimately, the effective utilization of data drives the evolution of autonomous vehicle technology, moving closer to the realization of fully autonomous transportation systems that are capable of operating reliably and safely in diverse real-world environments.
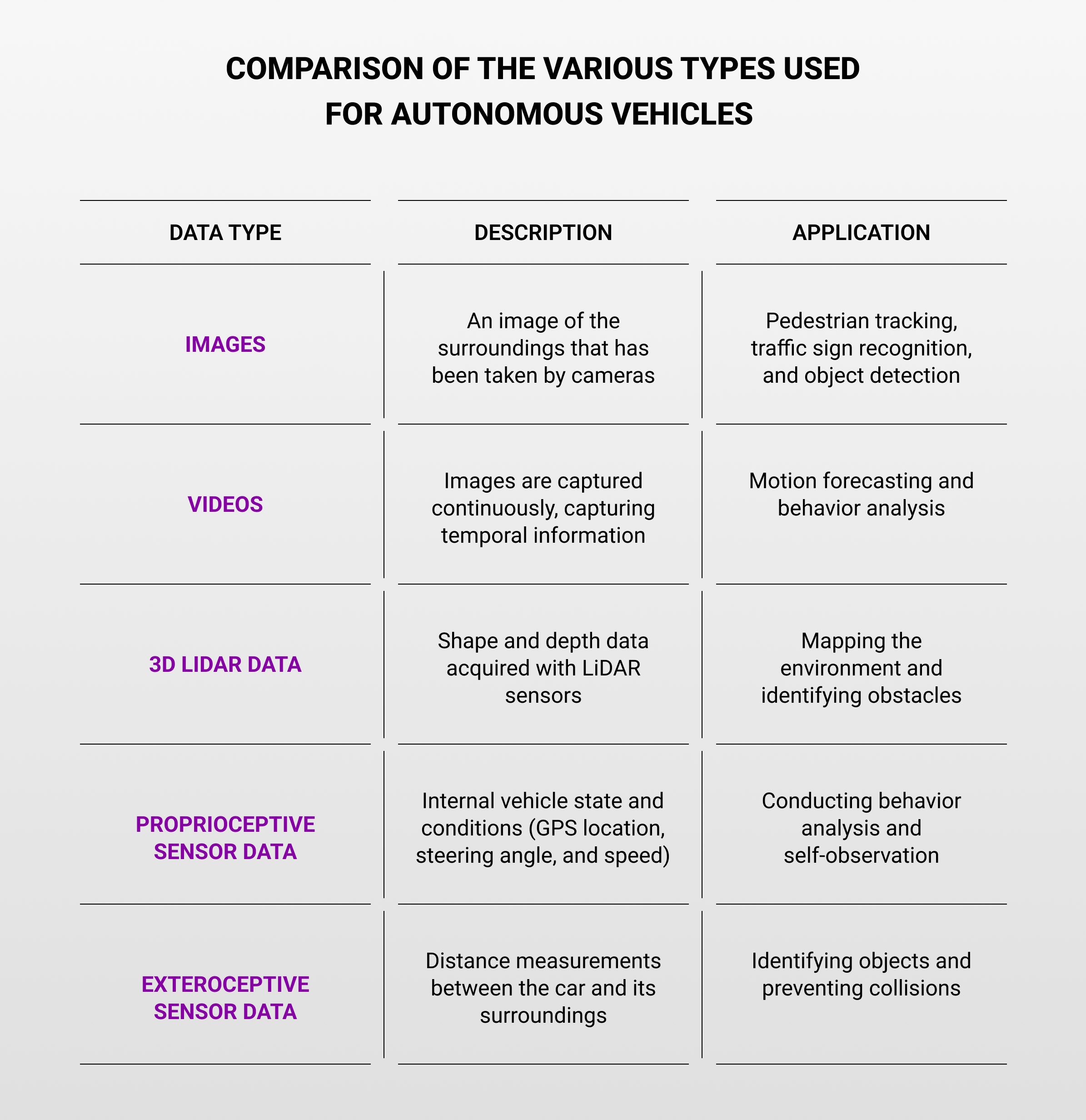
Comparison of the Various Types Used for Autonomous Vehicles
What Objects Are Annotated for Autonomous Driving?
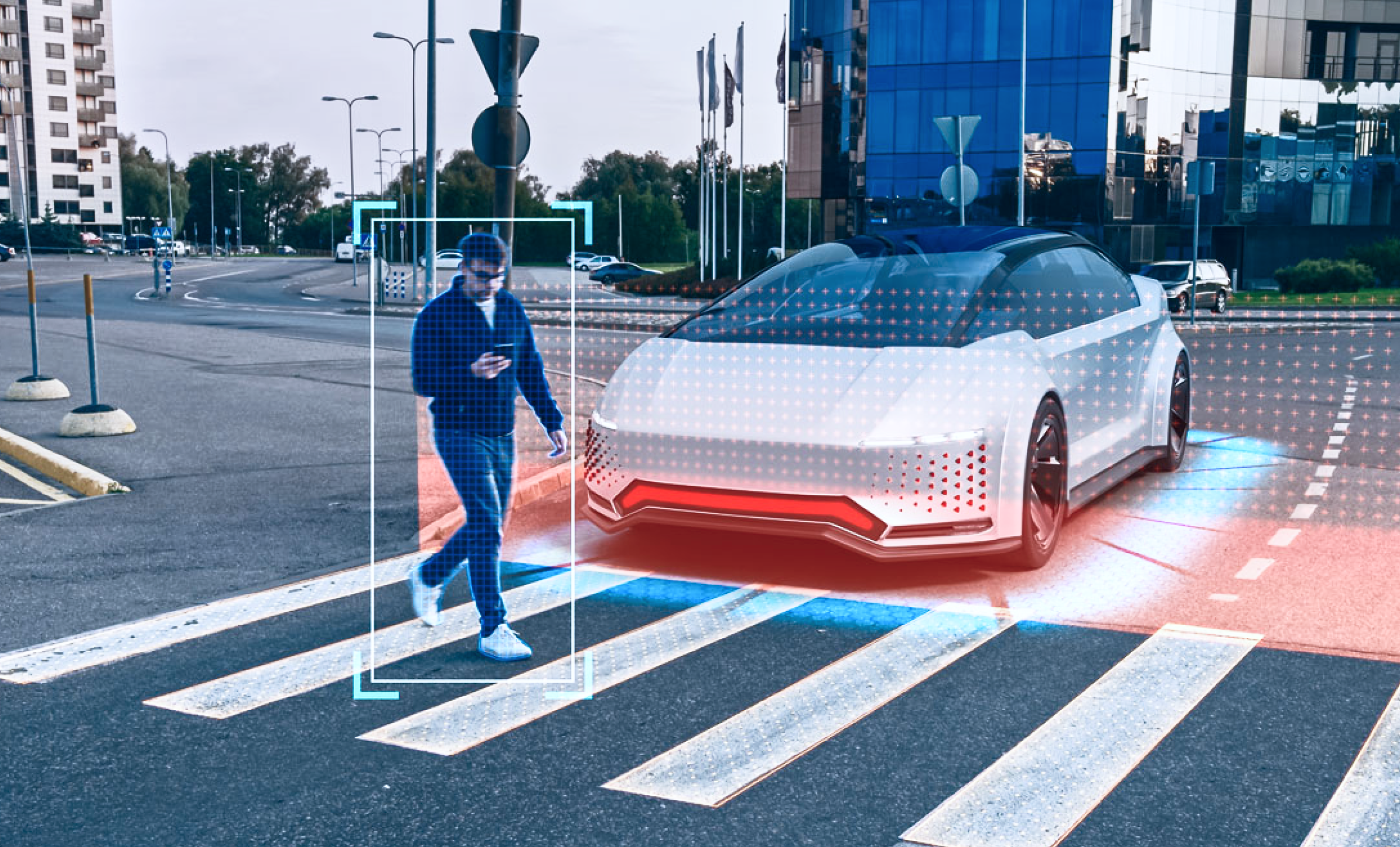
In the context of autonomous driving, various objects are annotated to enable vehicles to understand and navigate their surroundings effectively. Some of the key objects that are typically annotated include:
- Vehicles – Annotating other vehicles is crucial for autonomous vehicles to detect and track nearby cars, trucks, motorcycles, bicycles, and any other moving vehicles on the road.
- Pedestrians – Pedestrians, including adults, children, and animals, need to be accurately annotated to ensure the vehicle can detect them and predict their movements to avoid collisions.
- Cyclists/Pedestrians – The annotation of cyclists and pedestrians is essential for autonomous vehicles to identify and predict the behavior of cyclists sharing the road, including their speed, direction, and potential interactions with other traffic.
- Road Signs and Traffic Signals – Annotating road signs, traffic lights, and other traffic signals enables autonomous vehicles to recognize and interpret regulatory information such as speed limits, stop signs, traffic signals, and lane markings.
What Types of Data Annotation Are Used for Self-Driving Cars?
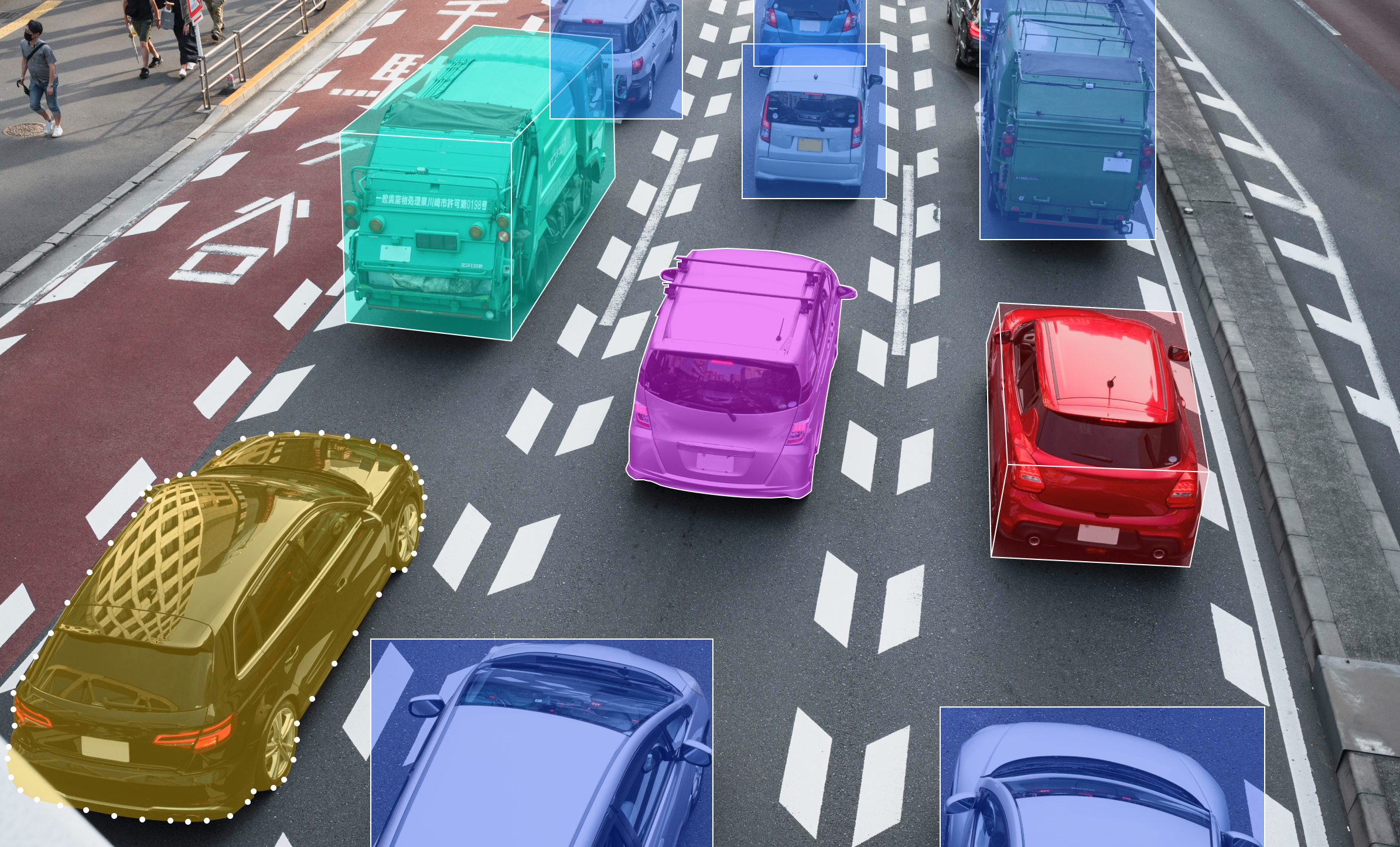
Several types of data annotation techniques are used for self-driving cars to label and annotate various elements within sensor data. Some of the common types of data annotation methods include:
- Bounding Boxes – Bounding boxes are rectangular shapes drawn around objects of interest, such as vehicles, pedestrians, cyclists, and obstacles, to indicate their location and extent within an image or frame of sensor data.
- Polygon Segmentation – Polygon annotation involves outlining objects in images using polygonal shapes, enabling algorithms to differentiate between objects and backgrounds.
- Semantic Segmentation – Semantic segmentation involves labeling each pixel in an image with a corresponding class label, such as road, vehicle, pedestrian, or background, to provide detailed information about the different objects and regions present in the scene.
- 3D Cuboids – This data annotation method involves drawing cuboids around objects to enable the system to understand the dimensions of the object, which, in turn, helps the system better identify these objects in the future.
- Landmark and key points – Landmark annotation is a data annotation technique used in various fields, including computer vision and robotics, to label specific points or landmarks within an image or dataset. These landmarks are typically key points or distinctive features that are of interest to the task at hand.
Role Of Data Annotation For Autonomous Vehicles

The primary role of data annotation for autonomous vehicles includes:
- Object Detection – Object detection is a computer vision task that involves identifying and locating objects within an image or video frame. Unlike image classification, which assigns a single label to an entire image, object detection identifies multiple objects of interest within an image and provides information about their locations.
- Lane Detection – Annotating lane markings, road boundaries, and curbs help autonomous vehicles understand the layout of the road and stay within their designated lanes while navigating.
- Mapping and Localization – This involves labeling key features and landmarks within sensor data to create detailed maps and enable precise localization for autonomous vehicles. This process plays a crucial role in developing robust localization algorithms and mapping techniques that are essential for autonomous navigation.
- Projection and Planning – Projection and planning are essential components of autonomous vehicle systems, enabling them to perceive their surroundings, predict future states, and make informed decisions to navigate safely and efficiently.
Why Do You Need Data Labeling for Autonomous Cars?
Data labeling is essential for training machine learning models, improving perception and recognition, enhancing decision-making, ensuring safety and reliability, adapting to varied environments, and facilitating iterative improvement in autonomous cars. Without data labeling, the development and deployment of autonomous driving systems would be severely limited, hindering their ability to operate safely and effectively on public roads.
How Mindy Support Handles Autonomous Vehicle Data
Mindy Support’s annotation of autonomous vehicle data involves labeling various elements within sensor data to provide contextual information for training machine learning models and improving the vehicle’s perception and decision-making capabilities. We are well-versed in various data annotation tools to label objects, obstacles, road markings, and other elements within the dataset. These tools may include graphical user interfaces (GUIs), custom software, or third-party annotation platforms. We also offer quality assurance processes to ensure accuracy and consistency. This may involve reviewing annotations for errors, verifying label placements, and resolving discrepancies between annotators.
Concluding Thoughts on AI-Assisted Driving and The Value of Data
Data annotation is indispensable for autonomous vehicles as it enables them to perceive their environment accurately, make informed decisions, ensure safety, adapt to diverse conditions, and continuously improve their performance over time. Without data annotation, the development and deployment of autonomous driving systems would be severely limited, hindering their ability to operate safely and effectively on public roads.
FAQ
1. What is data annotation, and why is it important for autonomous vehicles?
Data annotation involves labeling various elements within sensor data, such as objects, road markings, and obstacles, to provide contextual information for training machine learning models. It’s crucial for autonomous vehicles as it enables them to accurately perceive their environment and make informed decisions while navigating.
2. What types of data are annotated for autonomous vehicles?
Data annotation for autonomous vehicles typically involves annotating objects such as vehicles, pedestrians, cyclists, traffic signs, and road markings, as well as other relevant elements within sensor data captured by cameras, LIDAR, radar, and GPS.
3. How is data annotation performed for autonomous vehicles?
Data annotation for autonomous vehicles is typically performed using specialized annotation tools that allow annotators to label objects, draw bounding boxes, and assign class labels within sensor data. Annotators may also annotate attributes such as object speed, direction, and size.