How to Use Artificial Intelligence in the Healthcare Industry
Artificial intelligence is transforming the healthcare industry, offering new ways to improve patient care, streamline operations, and accelerate medical research. From predictive analytics that help identify at-risk patients to intelligent systems that support clinical decisions, AI tools are becoming essential to modern healthcare. As the technology continues to evolve, healthcare providers are finding innovative uses for AI in areas like diagnostics, treatment personalization, and operational efficiency. This article explores the numerous ways AI and data annotation in healthcare can be applied in healthcare, highlighting practical strategies, AI in healthcare examples, and considerations for successfully integrating AI-driven solutions to enhance patient outcomes and support medical professionals.
Key AI Technologies in Healthcare
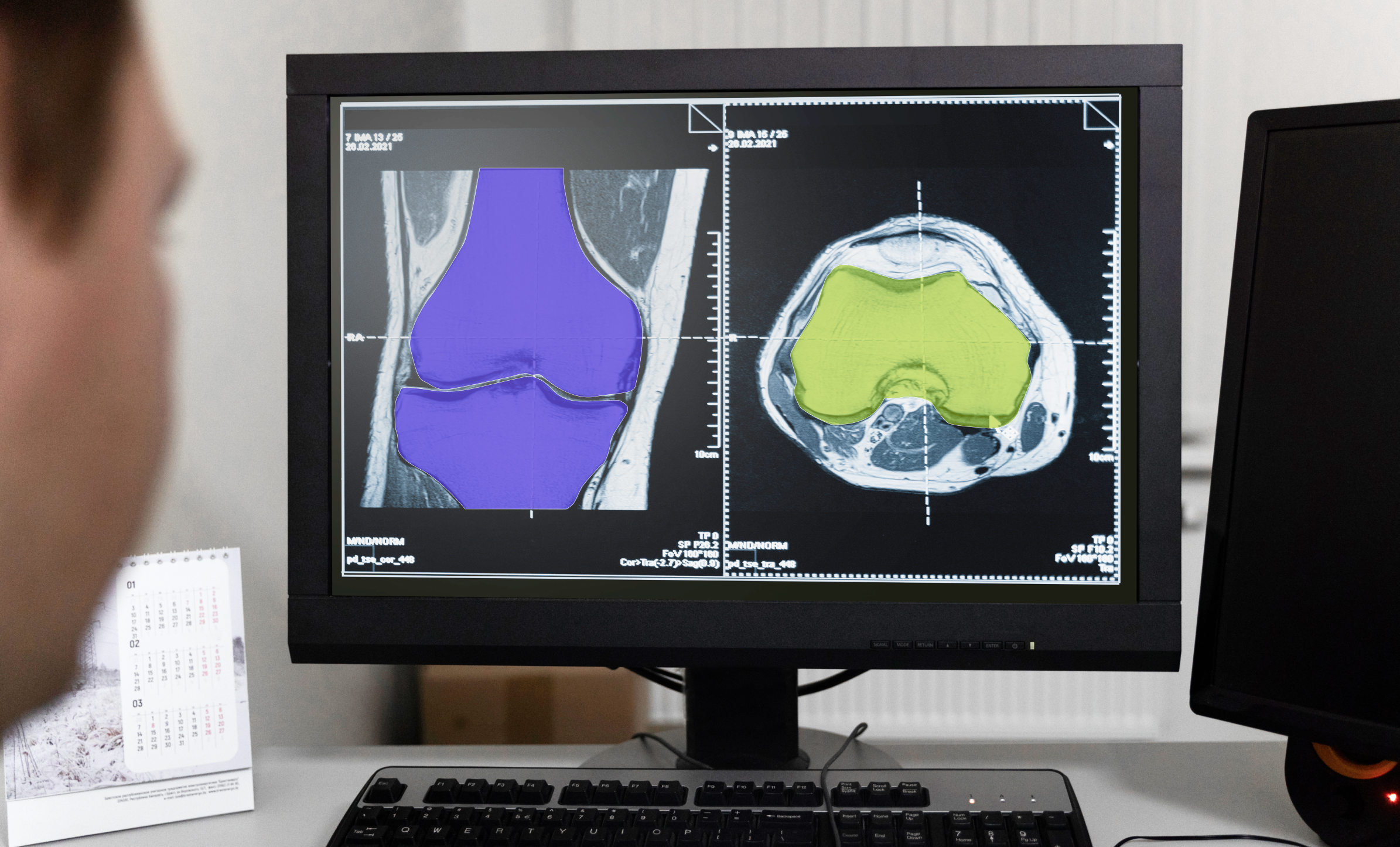
Artificial intelligence in healthcare is changing the way healthcare is offered to patients by providing advanced tools that enable more precise, efficient, and personalized medical services. Machine learning (ML) and deep learning, for instance, allow systems to analyze vast amounts of patient data to identify patterns, predict disease progression, and tailor treatments to individual needs. Natural language processing (NLP) is another transformative technology, enabling AI to interpret unstructured data in medical records, clinical notes, and research documents, making it easier for healthcare professionals to retrieve and apply relevant information.
Computer vision is also playing a significant role, particularly in imaging diagnostics, where AI-powered systems assist radiologists by detecting anomalies in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with remarkable accuracy. Robotic process automation (RPA) is streamlining administrative tasks, reducing human error, and freeing up medical staff to focus on patient care. Together, these AI healthcare technologies are reshaping healthcare by enhancing decision-making, improving patient outcomes, and making medical workflows more efficient.
Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics
Machine learning (ML) is driving significant advances in predictive analytics within healthcare, empowering providers to anticipate patient outcomes and make proactive decisions. By analyzing extensive datasets, including patient histories, lab results, lifestyle factors, and genetic information, ML algorithms can identify patterns that signal potential health risks before they fully manifest. An example application of AI in healthcare is predictive models that can assess a patient’s likelihood of developing chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or even certain cancers, enabling early intervention and personalized care plans.
Furthermore, ML-driven predictive analytics aids hospitals in resource planning, helping to forecast patient admissions, optimize staffing, and allocate medical resources more effectively. This predictive approach not only enhances patient care but also reduces healthcare costs and supports more sustainable, efficient healthcare systems.
Administrative Applications of AI
In healthcare, artificial intelligence is streamlining the administrative processes, and making medical staff more efficient and less burdened with its redundant routine tasks. By using robotic process automation (RPA), AI can handle personal tasks like patient scheduling, billing and claims handling thereby shortening your time and the likelihood of human error. Patient inquiries, appointment reminders and follow ups are also being managed by using AI driven chatbots and virtual assistants which increases patient engagement, and helps prevent missed appointments. These are important examples of how AI is used in healthcare.
This way, healthcare providers are able to quickly access much needed patient data because the technologies use natural language processing (NLP) to automate the extraction and structuring of information found in medical records. By removing these administrative functions away from the professional health care staff, AI eliminates the need to spend time on these operations, thereby freeing up health professionals to concentrate on patient care directly and smoothing out the operation costs.
Improving Hospital Operations
You may be wondering where is AI used in healthcare? AI is transforming hospital operations by optimizing workflows, resource allocation, and overall efficiency. Predictive analytics help hospitals anticipate patient admission rates, enabling better planning for bed occupancy, staffing, and equipment needs, which is especially valuable during peak times or crises. In logistics, AI-powered systems streamline inventory management, ensuring essential supplies and medications are restocked accurately and promptly.
Additionally, AI in healthcare use cases include AI-based scheduling systems that enhance operating room utilization by reducing scheduling conflicts and minimizing downtime, improving both patient throughput and satisfaction. AI also contributes to facility management, with smart sensors monitoring and adjusting lighting, temperature, and even sanitation processes, creating a safer and more comfortable environment for patients and staff. Together, these AI-driven advancements allow hospitals to operate more effectively, reduce costs, and enhance patient care.
Challenges of AI for Healthcare Implementation
Implementing AI in healthcare comes with several key challenges, including:
- Data Privacy and Security – AI requires access to sensitive patient data to function effectively, raising concerns about data security, patient privacy, and compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA. Ensuring that data remains secure and confidential is crucial to prevent breaches and maintain patient trust.
- Data Quality and Standardization – For AI to deliver accurate results, it needs high-quality, standardized data. However, healthcare data is often inconsistent, incomplete, or unstructured, which can hinder the reliability and effectiveness of AI models and limit the potential benefits of AI-driven insights.
- Integration with Existing Systems – Many healthcare facilities rely on legacy systems that may not easily integrate with modern AI tools. Implementing AI often requires significant infrastructure updates, system interoperability efforts, and additional costs, making it a challenging endeavor for many institutions.
- Skill Gaps and Training Needs – AI adoption requires healthcare professionals to be trained on new technologies, which can be time-consuming and costly. Additionally, there is a shortage of specialized skills needed to develop, implement, and maintain AI systems, which can delay or complicate AI adoption in healthcare.
- Ethical and Legal Concerns – The use of AI in healthcare raises ethical issues, particularly around decision-making and accountability. For instance, if an AI system makes an incorrect diagnosis or treatment recommendation, it may not be clear who is responsible—the AI developer, the healthcare provider, or the institution. Ensuring transparent and fair AI decision-making processes is essential to avoid bias and protect patient rights.
Data Privacy and Security
In healthcare, one of the most sensitive types of data to be processed can be done only with the help of AI solutions in healthcare, so data privacy and security are paramount. Depending on the use case, AI systems need access to large volumes of different types of data including personal health records, diagnostic histories, genetic information and more, to predict accurately and to provide personalized care. This though creates a dependency on data and the possibility of breaches, unauthorized access and misuse of personal information.
Nevertheless, this ensures compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR in order to protect patient rights and maintain trust in the industry. It is essential to encrypt your data, secure it, and prevent access, but it also means making it more complex to deploy AI. Moreover, anonymization or de-identification of data for the purpose of AI processing is feasible for preserving patient privacy but inherently a technically challenging task. Of course, these amazing applications we create from effectively impeding data from uninvited sources require ongoing efforts in incorporating more cybersecurity measures and implementing existing protocols protecting privacy.
Benefits of AI in Healthcare
AI offers numerous benefits to healthcare, enhancing patient care, streamlining processes, and advancing medical research. Key benefits include:
- Improved Diagnostics and Accuracy: AI algorithms can analyze medical images, genetic information, and patient histories with high precision, assisting healthcare providers in early and accurate diagnosis of conditions like cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders.
- Personalized Treatment: AI enables personalized care by analyzing individual patient data to tailor treatment plans based on specific risk factors, genetic markers, and lifestyle, which improves patient outcomes and minimizes adverse effects.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: AI automates administrative tasks such as scheduling, billing, and claims processing, reducing human error and freeing up healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
- Predictive Analytics for Preventive Care: AI-driven predictive models help identify at-risk patients before they develop serious conditions, allowing for early interventions and reducing the likelihood of costly, intensive treatments down the line.
- Accelerated Drug Discovery and Research: AI accelerates drug development by analyzing large datasets to identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy, significantly reducing time and costs in the pharmaceutical industry.
Better Patient Care and Outcomes
Not only can AI be used in healthcare, but it is powering a more accurate, timely and personalized patient care that ultimately leads to better patient outcomes. AI through its predictive analytics model can predict those people who engage in a chronic disease or complication can facilitate the healthcare providers to take early preventive measures as they are specific to the patient’s unique profile. Machine learning algorithms can suss out the patterns and anomalies in vast quantities of data that might be overlooked by traditional diagnostics and increase the accuracy of diagnosis of things like cancers or rare genetic diseases.
AI can also help in treatment personalization by combining genetic, lifestyle and the history data to suggest personalized treatment plans with enhanced effectiveness and reduced side effects. Beyond these direct applications to patient care, AI-driven tools are used for clinical decision making that helps health care providers make more informed, faster, more confident decisions. Taken together these advancements cut readmission rates to the hospital, reduce medical errors, and generally produce higher quality care that is better for the long term health of patients.
The Future of AI in Healthcare
AI in healthcare is about more than just AI devices in healthcare. The more AI technologies advance, the more sophisticated, and more seamless, we can expect integrated with electronic health records (EHR) that allow real time analysis of data and personalized treatment plans. But as telemedicine and wearable health devices continue to rise, AI will play an increasingly important role as patients can be constantly monitored and the data can be analyzed continuously and come up to proactive care and timely intervention. Also, natural language processing will enhance AI’s ability to understand and summarize difficult medical literature used by clinicians to keep up with the most recent research and therapy plans.
Healthcare provider companies equipped them with combined human expertise and machine learning capabilities, so called ‘Collaborative AI Systems’, that will make more informed decisions to have better patient outcomes and increased operational efficiencies. Data from the UK, U.S., and Europe suggest that as AI becomes an increasingly central part of health system policy, more healthcare organizations will invest in the infrastructure and training required to leverage AI while also addressing the ethical and privacy concerns in play. This should accelerate the integration of AI into everyday health system practices and yield a more efficient, accessible, and personalized system.
Conclusion
The integration of artificial intelligence in healthcare represents a transformative shift that promises to enhance patient care, streamline operations, and foster innovation in medical research. While the benefits of AI—such as improved diagnostics, personalized treatment plans, and increased operational efficiency—are significant, challenges like data privacy, system integration, and ethical considerations must be carefully navigated. As technology continues to evolve and regulatory frameworks adapt, the potential for AI to reshape the healthcare landscape grows. By embracing AI thoughtfully and collaboratively, healthcare providers can not only improve outcomes for patients but also create a more efficient and effective healthcare system that meets the demands of the future. As we look ahead, the successful implementation of AI in healthcare will depend on continued investment in technology, education, and ethical practices, ensuring that the benefits of AI are realized for all stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem.