How Data Annotation is Used to Train Robots to Pick Apples
Robots across industries have already achieved an impressive level of automation. They can sort packages at warehouses, help build cars at factories, and there are even robotic dogs that can make great pets. However, there are still some basic tasks that robots cannot do, such as picking apples from a tree. If a robot could learn to pick apples without damaging them, this would alleviate a lot of time-consuming work off the shoulders of farmers. Today we will learn about the benefits of creating such AI technology and the data labeling required to train them.
Why Do We Need Apple-Picking Robots?
For a human, picking an apple is relatively simple. Just reach into a tree, feel around, touch it, and say, “Hey, this is an apple, and its stem is right here.” Pull and twist on the stem to pick the apple from the tree and place it in the right basket. Researchers have placed a lot of effort into creating a robot that can not just pick the apples but also place them into a bin without damaging them, i.e., the robot cannot squees the apples too hard, through them in the been rough manner, etc. While many creative approaches have been tried before, an AI-based approach is best because it aims to replicate human movements with robotic fingers.
If successful, such technology could transform agriculture, turning fruit-picking – a backbreaking, time-consuming human task – into one that’s speedy and easier on farmworkers. To put this into perspective, the average size of a United States orchard is 50 acres, and apples harvested from an average tree can fill 20 boxes that weigh 42 pounds each. As you can imagine, apple picking is quite a time-consuming process requiring a lot of human labor.
These efforts have become more relevant in recent years given the deteriorating working conditions on farms caused by climate change, such as extreme heat, wildfires, and the smoke that comes from them, as well as the shortage of qualified workers to actually do the work. Therefore, should such an AI robot be created, it would improve the overall working conditions as well as worker safety, although a lot will depend on how efficiently the farmers use the robots in the fields.
How Can We Create a Robot That Can Pick Apples?
To train robots to pick apples, researchers needed to change the appearance of the traditional orchard. The reason for this is that they usually contain irregularly shaped trees and giant canopies. Shifting sunbeams, fog, and clouds add to computer vision which poses too big of a hurdle for the AI system and the algorithms that power them to overcome. In fact, such tall and winding trees are challenging even for human apple pickers since they need to spend additional time carrying and adjusting the ladder into the right position to grab the apples. This is why researchers training such AI technology have shifted to orchards where trees grow flat against trellises, their trunks and branches at right angles to create a “wall of fruit.” The thinner canopy also lets more sunlight in, encouraging fruits to form.
The AI robot, which is essentially a giant arm mounted on a rolling platform, takes about five seconds to pick an apple. It has picked an apple successfully about half of the 500 or so times it has tried so far. Still, the robotic arm has cracked some problems that posed hurdles to automation. For instance, it can avoid damaging both fruit and tree limbs in the harvesting process.
What Data Annotation Required to Create an Apple-Picking Robot?
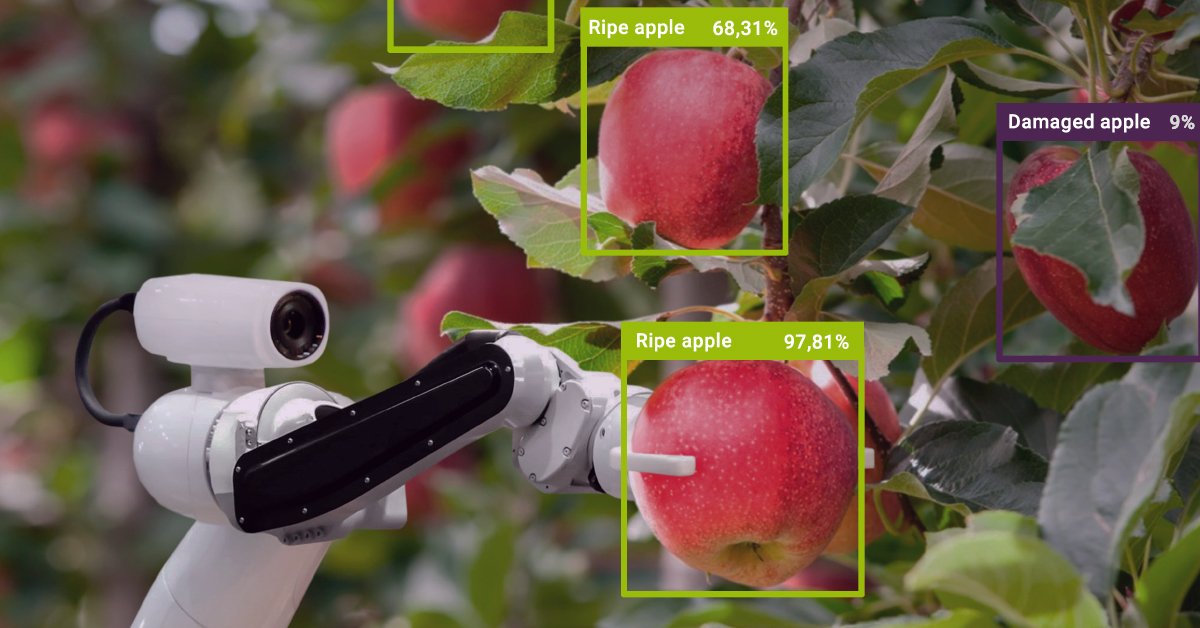
In order to pick the apple, the robot must first detect it with its computer vision cameras. This requires human data annotators to label apples of various shapes, colors, and sizes in images or videos. In addition to picking the apples, the robot needs to navigate the orchard and avoid running into trees. This would require 3D Point annotation, which would allow the robot to orient itself in the surrounding environment and understand the distance between itself and an object next close or far away from it.
Trust Mindy Support With All of Your Data Annotation Needs
Mindy Support is a global company for data annotation and business process outsourcing, trusted by several Fortune 500 and GAFAM companies, as well as innovative startups. With nine years of experience under our belt and offices and representatives in Cyprus, Poland, Romania, The Netherlands, India, and Ukraine, Mindy Support’s team now stands strong with 2000+ professionals helping companies with their most advanced data annotation challenges.