How AI Systems Rely on LiDAR to Navigate Their Surrounding
While LiDAR is often associated with autonomous vehicles, AI robotic systems, in general, rely on LiDAR to navigate their surroundings. For example, AI-powered robots are often used in the agriculture area to perform mundane tasks like picking ripe fruits and vegetables, removing weeds, and other activities. As we shall see later on, Mindy Support has worked on a LiDAR project to identify noise walls and signs on railroads. Before we get into the use cases, let’s first get an understanding of what LiDAR actually is.
What is LiDAR?
LiDAR is an acronym for “light detection and ranging”. LiDAR is similar to traditional radar since it sends out pulses of electromagnetic radiation to detect objects in its surroundings. These lasers bounce off the objects and return back to the car which allows the system to measure the distance. LiDAR offers ultra-fast response time to allow the AI system to make quick decisions to react to changing circumstances on the road. The biggest advantage of LiDAR is the accuracy it offers.
LiDAR images produce a 3D Point Cloud which is a representation of how the computer sees the physical world. This also needs to be annotated to label all of the items in the image and their distance from the vehicle. This is usually done with colors representing short and long wavelengths. For example, when working with 3D Point Clouds for the automotive sector, the road on the 3D Point Cloud will always be blue since this color has a short wavelength and the road itself is the lowest point on the image.
How Does LiDAR Work?
LiDAR sends out many pulses of lights that bounce off any objects within the vicinity and return back to the LiDAR. The longer it takes the light to travel, the farther away the object is located and vice-versa with objects within close proximity. All of this creates a 3D Point Cloud which is a digital representation of the way the LiDAR views the physical world. This 3D Point Cloud needs to be annotated with methods like tagging and semantic segmentation if the images will be color-coded. For example, the color blue has a short wavelength so the ground will always be blue because it’s the closest to the LiDAR. Farther away objects will be red or orange since these colors have a long wavelength.
What are the Pros and Cons of LiDAR?
Just like with any technology, LiDAR has its pros and cons. Let’s start with the pros:
- Accuracy – Short wavelengths can detect very small objects allowing companies to create more accurate 3D models.
- Speed – The amount of time it takes a pulse of light to travel from the LiDAR, bounce off an object and return back to the LiDAR is less than a second. This makes it possible to scan large areas within a short period of time.
- It is possible to collect from a variety of locations – Places such as mountains, wooded areas can be hard to reach with other technologies, but can be easily mapped with LiDAR
- High level of automation – Once the LiDAR starts working it pretty much does not require any human intervention to operate.
The cons of LiDAR include:
- High cost of equipment – LiDAR itself can be very expensive. In fact, if we take a look at the automotive sector, an autonomous car equipped with LiDAR might cost around $180,000.
- Difficulties in bad weather conditions – Since LiDAR uses visible lasers in order to measure distance, it will not be able to work in bad weather conditions such as heavy snowfall or rain.
- LiDAR consumes a lot of energy – Since LiDAR consumes so much energy, it may decrease the ability of the car, drone, or robot to travel long distances.
- LiDAR is not visually appealing – If we look at the LiDAR used by companies like Waymo, it is a large box on top of the roof of a car. This does not look very appealing to a buyer, especially if the car is already very expensive.
Why is Often Used Despite the Drawbacks?
LiDAR is still the most popular technology to enable robots to see the real world because it is the most accurate. If we look at the competitors of LiDAR, like Radar, for example, Radar sends out radio waves, whereas LiDAR sends out light waves. However, radio waves have a larger wavelength than light waves and they are not suitable for detecting small objects, like things an autonomous vehicle might encounter on the road. This is why Radar is mostly used for military purposes to detect large vessels and vehicles.
If we look at Tesla, which uses a system of cameras, called the Hydranet instead of LiDAR, this is also not as reliable as LiDAR. The reason for this is that to use just cameras, you must understand an image at a level approaching how humans do with our eyes and brains. LiDAR offers the superhuman ability to know exactly how far away everything is inherently and it is almost perfect at doing so.
How and Where is LiDAR Used?
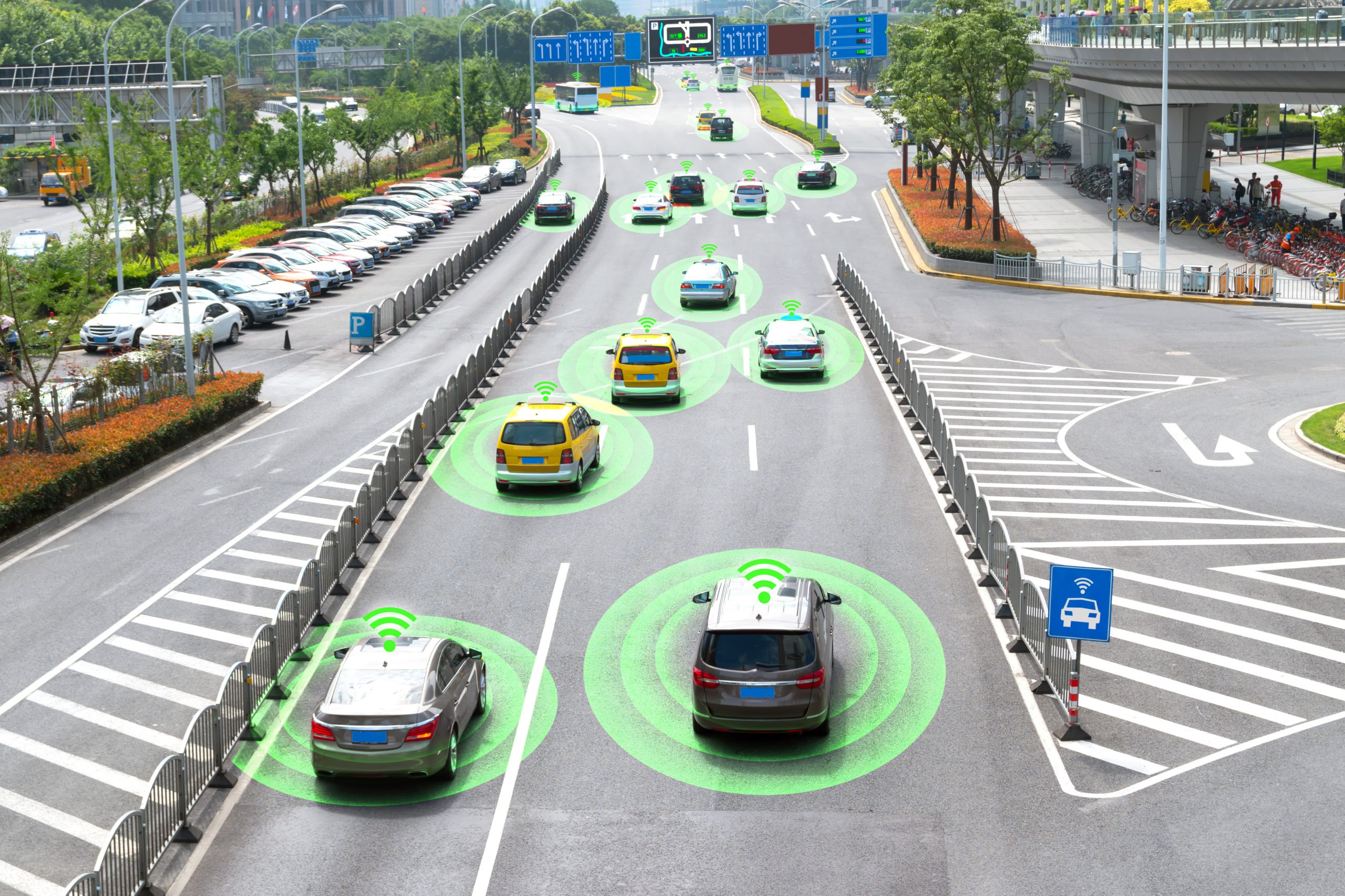
LiDAR is widely used in the automotive world to create autonomous vehicles. We go into this in great detail in the next section. One of the most interesting uses of LiDAR that many people may not be aware of is in our smartphones. The latest iPhone 12 Pro and the iPhone 12 Pro Max use LiDAR to power the built-in measuring app. It allows you to measure distances more accurately to map out three-dimensional spaces. There are also many apps that use LiDAR, like the IKEA app that allows you to take any item in the catalog and superimpose it on real-world surfaces using AR. The LiDAR allows for more accurate dimension measurements to show you how much space the item will take up, which makes it easier to determine whether or not it will be a good fit.
LiDAR is also widely used in the robotics industry to allow robots to see the real world. This allows researchers to create robots for the agriculture industry that pick ripe fruits and vegetables. In the healthcare industry there are all kinds of robots that interact with patients, deliver supplies, and many other uses.
LiDAR for Automotive
The days of autonomous cars on the road seem to get closer every year with new inventions and developments announced to make the car function correctly on the road. Most companies are using LiDAR along with cameras and radar to train the machine learning algorithms. We already mentioned that a 3D Point Cloud is essential to autonomous vehicles, but the algorithms constantly need to be perfected for self-driving cars to become mainstream. In fact, we are already seeing companies like Mitsubishi, Nissan, and other manufacturers implementing LiDAR in their 2021 and 2022 car models.
Now that we know what LiDAR is and how it works, let’s take a look at some use cases Mindy Support has worked in the LiDAR area.
Mindy Support’s Use Cases in LiDAR
The use cases below demonstrate some of the challenges involved in actualizing LiDAR project and having the right experience allowed us to overcome those challenges.
Detecting and marking traffic signs and traffic lights
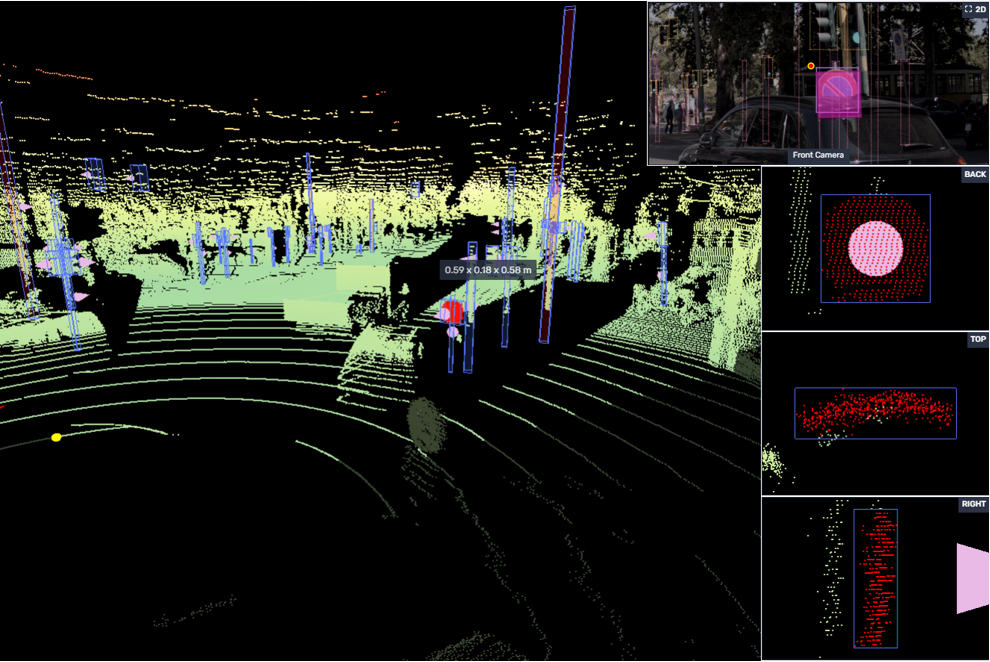
Country: Germany
Purpose: Detection and marking traffic signs and traffic lights with 3D Cuboids on the Lidar clouds and with Bounding boxes on 2D images.
Challenges:
1) Many objects per task, wide variety of signs to be labelled.
2) Some tasks were overloaded with objects to be annotated.
Solution: Additional Approve and Quality Control stages for maintaining the quality on the high level.
Team: 100 agents within 6 months
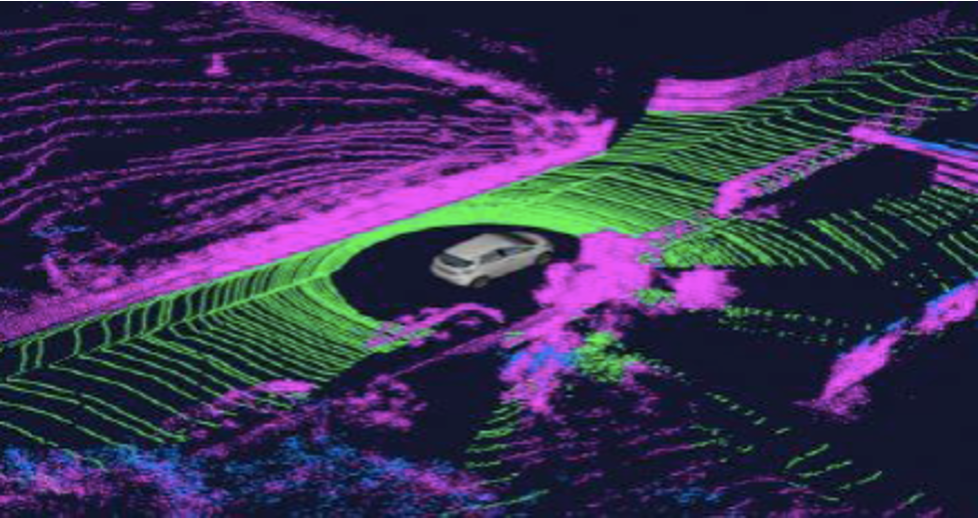
Multi-sensor linking: Identifying noise walls and signs on the railroad
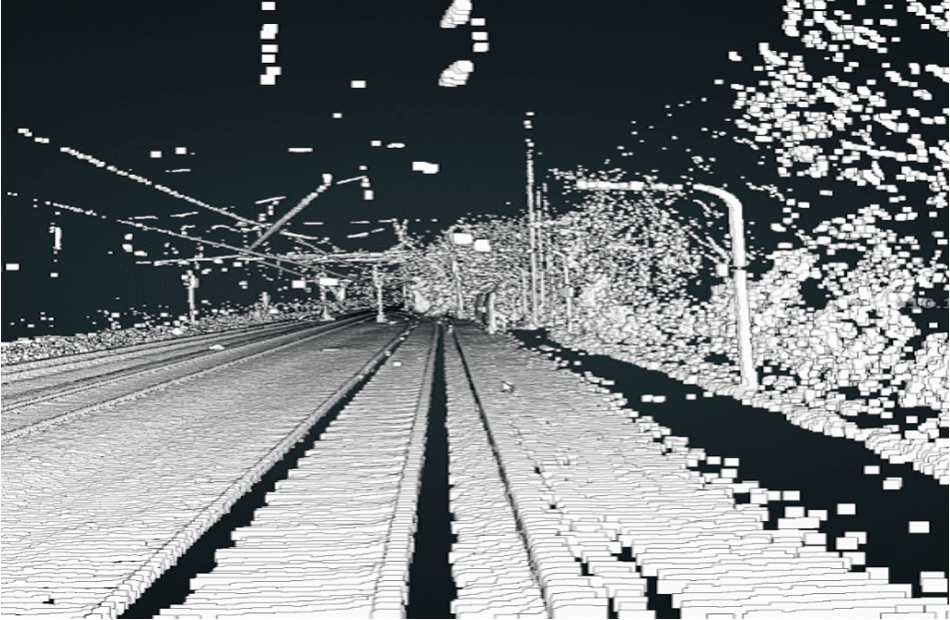

Country: Germany
Purpose: Make multi-sensor linking by Identifying noise walls and signs on the railroad.
Challenges:
1) There was no ready-made tooling solution that could meet all of the project requirements.
2) Connecting coordinates of objects in the point cloud images taken by the LiDAR with the real coordinates of these objects on the map.
Solution: Developed our own technical solution to provide the required result for the client within set time frame.
Team: 95 agents within 2 months
Detecting and marking traffic signs and traffic lights
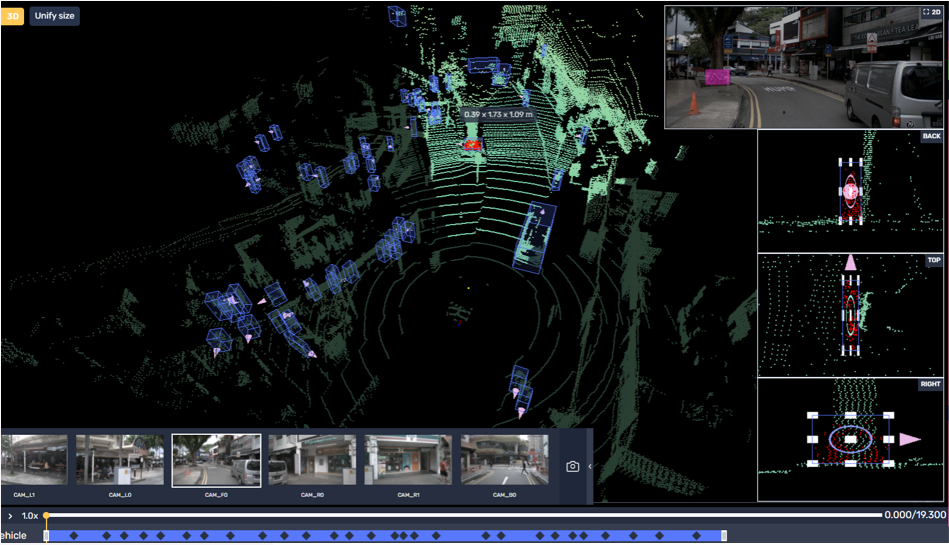
Country: Sweden
Purpose: Make point cloud segmentation, inter-frame data association and the track-level annotation.
Challenges:
1)Many objects to detect and track on the sequence of frames, including small objects.
2) Wide variety of categories and labels to be used.
Solution: Implemented multi-level training to strengthen skills of the team on 2D-3D object detections with the direction settlement and object’s interpolation.
Team: 80 agents within 7 months
Detecting and marking vehicles on sequences
Country: USA
Purpose: Detection and marking of vehicles on sequences with 50-70 frames, both LiDAR and 2D frames. Objects were captured from different positions
Challenge: Tracking each object on each frame within the whole sequence.
Solution: Prepared an extensive guide and conducted a multi-level training process to prepare the team to work with sequences in the most efficient way maintaining the high quality.
Team: 250 agents within 8 months
Detecting and marking traffic lights
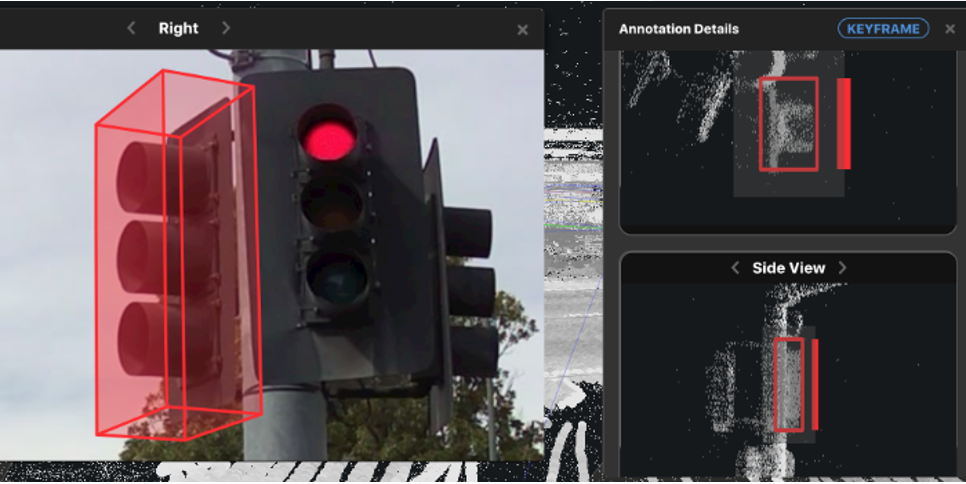
Country: USA
Purpose: Detection and marking traffic lights on the LiDAR sequences
Challenge: Detection of different traffic lights types and tracking each object on the whole sequence.
Solution: Adding extra examples on types of traffic lights and their distinctive features.
Team: 75 agents within 5 months
Verification of auto-generated polygons and determination of objects’ nature

Country: USA
Purpose: Verification of auto-generated polygons and determination of objects’ nature, using multi-camera views.
Challenge: Variety of small and occluded objects, which were difficult to determine.
Solution: Expanded the guide with more detailed explanations on how to determine objects correctly and how to work with sequences of frames in the most efficient way.
Team: 105 agents within 4 months
Trust Mindy Support With Your LiDAR Data Annotation Needs
As we have seen in the use cases above, Mindy Support has extensive experience in the areas of LiDAR and 3D Point Cloud Annotation. We are one of the largest BPO providers in Eastern Europe with more than 2,000 employees in six locations all over Ukraine. Regardless of the amount of data you need to be annotated, we can assemble a team that will get the job done within the specified time period. Our rigorous QA process ensures that all tasks are done correctly the first time around which allows us to scale your team without sacrificing the quality.