Cutting Edge New ADAS Capabilities Powered By Computer Vision Cameras
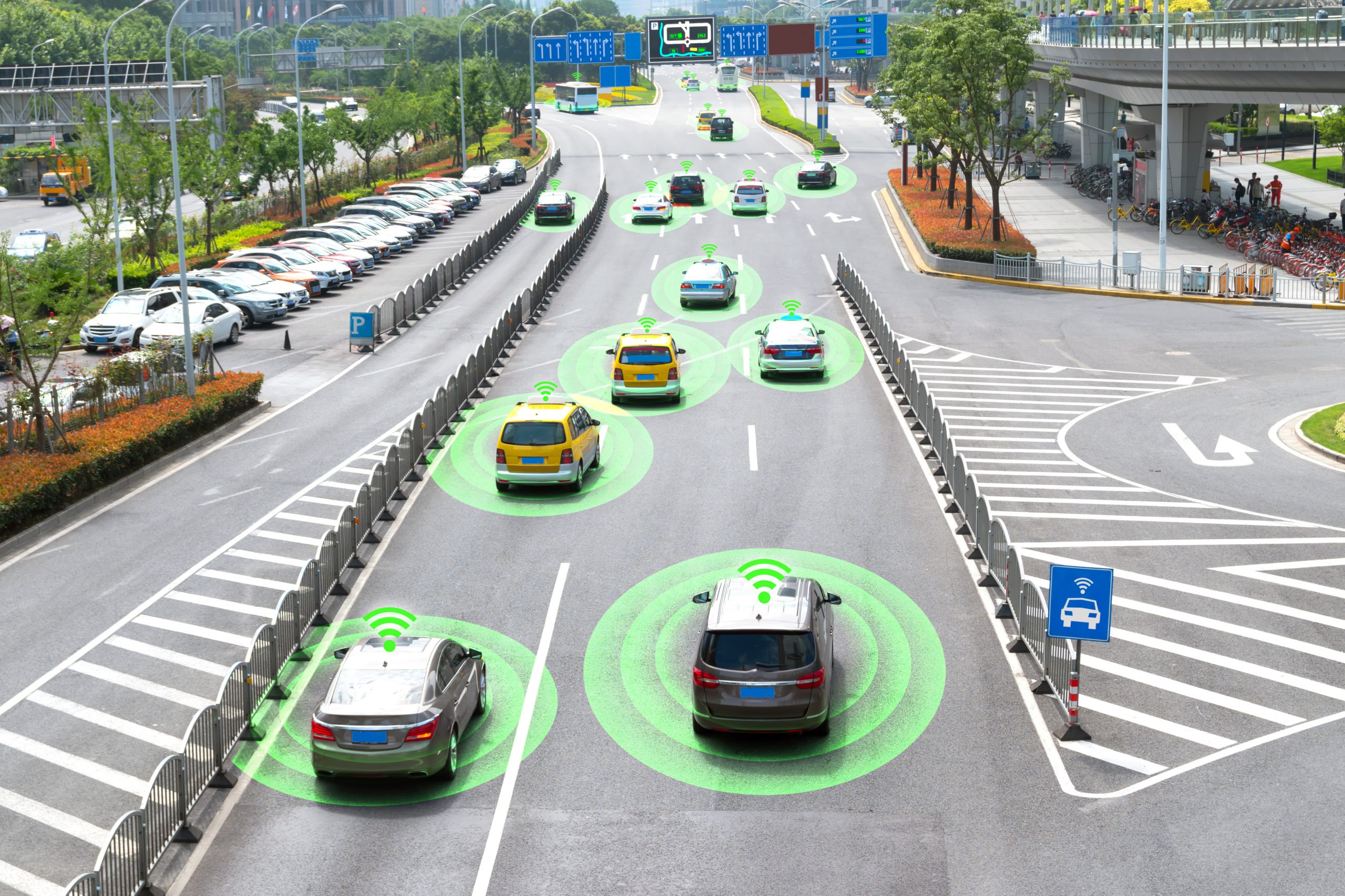
The development of autonomous vehicles is moving full speed ahead, with some of the most cutting developments coming from companies you might not expect. While companies like Tesla, Waymo, and other big market players, Xpeng, an autonomous vehicle developer from China, is rolling out some compelling new features. Let’s take a look at some of the latest technology that is hitting the market this year, as well as the data annotation that’s required to create them.
A Navigation Guided Autopilot
Xpeng plans to roll out a navigate autopilot (NGP) this year and into the first half of 2023 in certain Chinese cities. City NGP allows the car to semi-autonomously navigate complex urban environments with features such as lane switching. This is an interesting new advanced driver-assistance system (ADAS) which refers to a system that offers some autonomous capabilities, but still requires a driver.
The way the whole thing works is as follows. A driver will need to watch a safety video before being able to turn on Xpeng’s highway driving function. Drivers need to keep their hands on the wheel while using the vehicle’s autonomous driving features. Users then input their destination into the map. The car will then begin to carry out some of the functions like lane switching by itself. Drivers will get a warning when they need to take manual control of the car, for example, during adverse weather conditions or a road accident. The cars are equipped with 14 cameras and other critical sensors that allow the AI system to see the road.
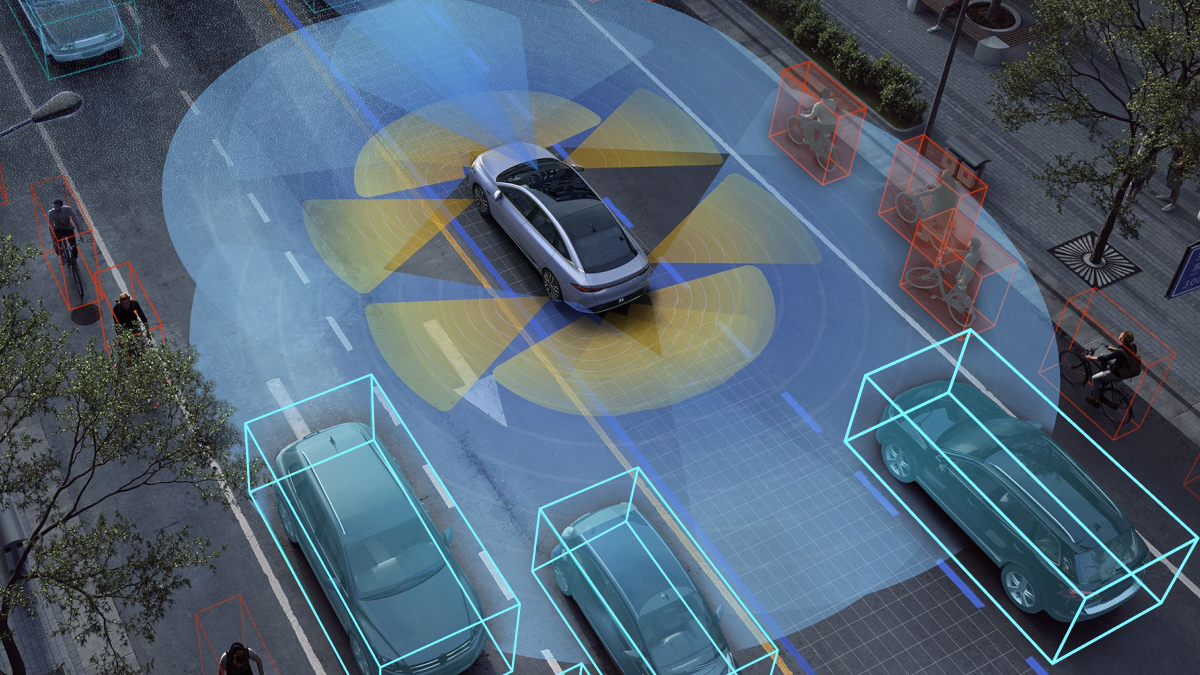

Using Cameras vs. LiDAR
We mentioned in the previous section that Xpeng is relying on AI cameras to enable the vehicle to see the road. This is interesting because most companies rely on LiDAR for such purposes. Now, the topic of Lidar vs. Cameras in autonomous vehicles is widely debated. The irony of these arguments is that these technologies rely on the same principle of electromagnetic emission, reflection, and reception of the sensors that complete it. However, the fundamental difference between Lidar and camera technology is that Lidar emits the light it sees, whereas cameras don’t. This gives Lidar the ability to calculate incredibly accurate distances to many objects that are simultaneously detected.
One of the primary advantages of LiDAR is accuracy and precision. In fact, companies like Waymo created their own LiDAR, which is so advanced that it can tell what direction pedestrians are facing and predict their movements. Another advantage of LiDAR is that it gives self-driving cars a three-dimensional image to work with. LiDAR is extremely accurate compared to cameras because the lasers aren’t fooled by shadows, bright sunlight, or the oncoming headlights of other cars.
Having said this, there are some advantages to using cameras. First, cameras are much less expensive than LiDAR systems, which brings down the costs of self-driving cars, especially for end-consumers. They are also easier to incorporate (modern Teslas have eight cameras around the car) since video cameras are already on the market. Tesla can simply buy the off-the-shelf camera and improve it rather than going out and inventing some entirely new technology. Cameras can also see the world in the same way as humans do and can, in theory, read street signs, interpret colors, etc., unlike LiDAR. Finally, cameras can easily be incorporated into the design of the car and hidden within a car’s structures, making it more appealing for consumer vehicles.
What Types of Data Annotation are Necessary to Allow the Vehicle to See the Road?
Since companies like Xpeng, Tesla, and many other manufacturers are equipping their vehicles with cameras, they would need all sorts of data annotation that has to do with computer vision. This can be something as simple as drawing 2D bounding boxes around the other cars on the road and other objects. If more information about the dimensions is required, then 3D bounding would need to be used. More advanced types of annotation may need to be used depending on the scope of the project, such as instance segmentation which tracks and counts the presence, location, count, size, and shape of objects in an image, and other types as well.
We also mentioned that LiDAR is also used in the development of autonomous vehicles. LiDARs create 3D Point Clouds which are digital representations of how the AI system sees the physical world. These 3D Point Clouds also need to be annotated with techniques such as 3D segmentation, which captures the motion of an object in a video, object classification, and many others.
Trust Mindy Support With All of Your Data Annotation Needs
Mindy Support is a global company for data annotation and business process outsourcing, trusted by several Fortune 500 and GAFAM companies, as well as innovative startups. With nine years of experience under our belt and offices and representatives in Cyprus, Poland, Romania, The Netherlands, India, and Ukraine, Mindy Support’s team now stands strong with 2000+ professionals helping companies with their most advanced data annotation challenges.