Autonomous Vehicles Help With Natural Disaster Relief
Acute natural disasters (e.g., atmospheric, hydrologic, geophysical, oceanographic, or biologic) can cause havoc and destruction in human society as well as in the natural world. In the geoscience and disaster risk reduction sectors, professionals frequently refer to such occurrences as natural disasters, since they disproportionately affect particular regions and populations. AI can help companies better manage the recovery from natural disasters and provide residents with relief faster. In this article, we will talk about the use of AI in natural disaster relief and the data annotation required to create it.
How Can AI be Used to Manage Natural Disaster Relief?
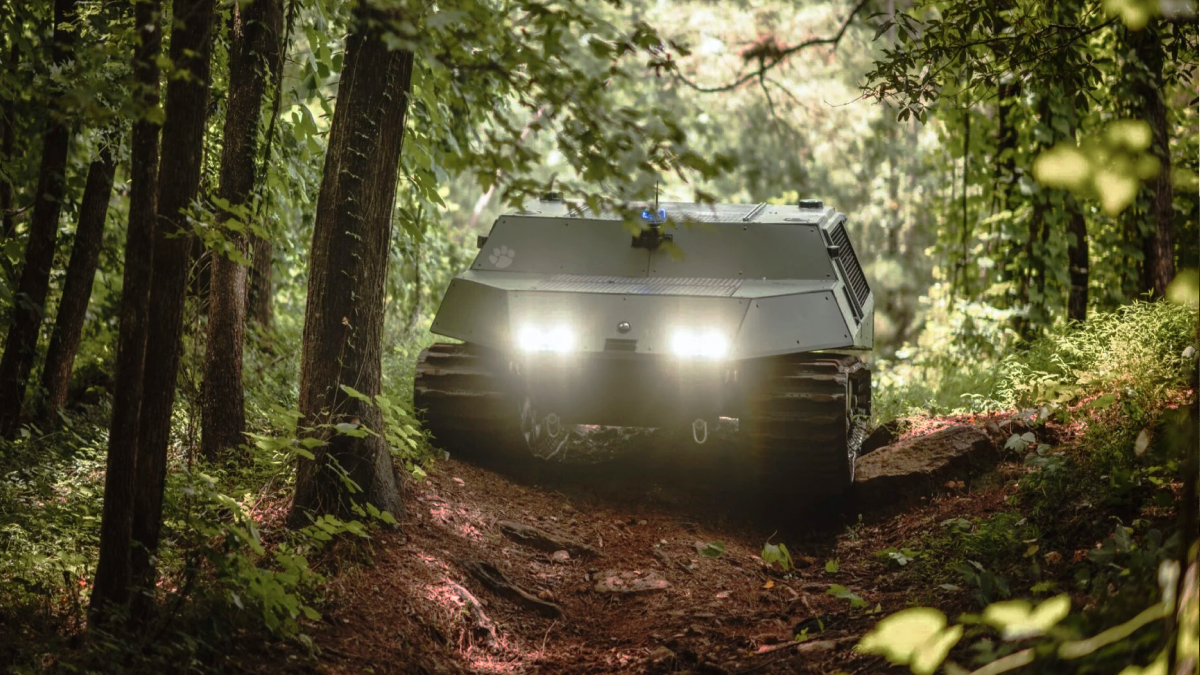

Natural disasters devastate the nation’s transportation infrastructure every year, disrupting distribution routes to affected communities and making it more difficult to assess the situation. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) of the United States, natural disasters alone cost the country $165.1 billion in damages in 2022. Students and researchers at Clemson University at the International Center for Automotive Research in Greenville, South Carolina, created an off-road reconnaissance and relief vehicle that can travel on its own to speed up the delivery of supplies and provide real-time data for emergency responders.
The autonomous vehicle can recognize and travel on uncharted terrain thanks to its high-accuracy GPS (GNSS) and LiDAR (light detection and ranging) systems. The vehicle can go at 45 mph, climb barriers that are 18 inches high, negotiate ground with a 60% grade, and pivot 360 degrees in place in two seconds. Its adjustable series-hybrid powertrain enables tremendous mobility, better fuel efficiency, and quiet operation while traveling solely on electricity. When the truck reaches its destination, it can transport emergency supplies and serve as a mobile generator in the event of power outages without endangering people.
Evaluating the Extent of the Damage
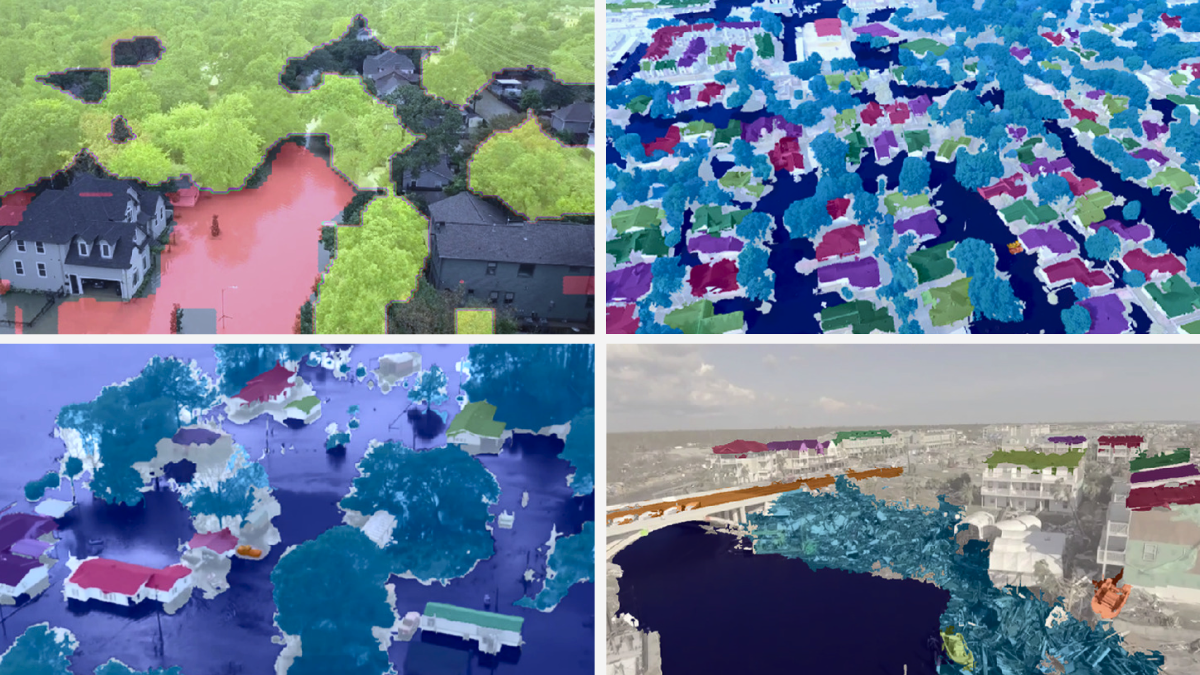
Another application of AI in natural disaster recovery is to identify building and infrastructure damage in the disaster area and categorize its severity much faster than is possible with current methods. This can help first responders and recovery experts on the ground quickly get an assessment that can aid in finding survivors and help coordinate reconstruction efforts over time. The algorithms use a method called semantic segmentation, which is akin to object recognition in that it assesses each individual pixel of an image and its connections to neighboring pixels to reach conclusions.
This is an advance over more conventional catastrophe assessment systems, which rely on eyewitness reports and requests for rescue and emergency personnel to swiftly determine where assistance is required. However, this can still take days, if not longer. In some more recent situations, fixed-wing aircraft like drones have flown over disaster zones with cameras and sensors to provide data assessed by people. The fact that many responding institutions frequently have their own walled data catalogs slows down the conventional response even more, making it difficult to develop a uniform, common understanding of which areas require assistance. Organizations may organize and prioritize their reactions with the aid of AI in a matter of minutes, saving time and lives.
What Types of Data Annotation are Needed to Train This AI Technology?
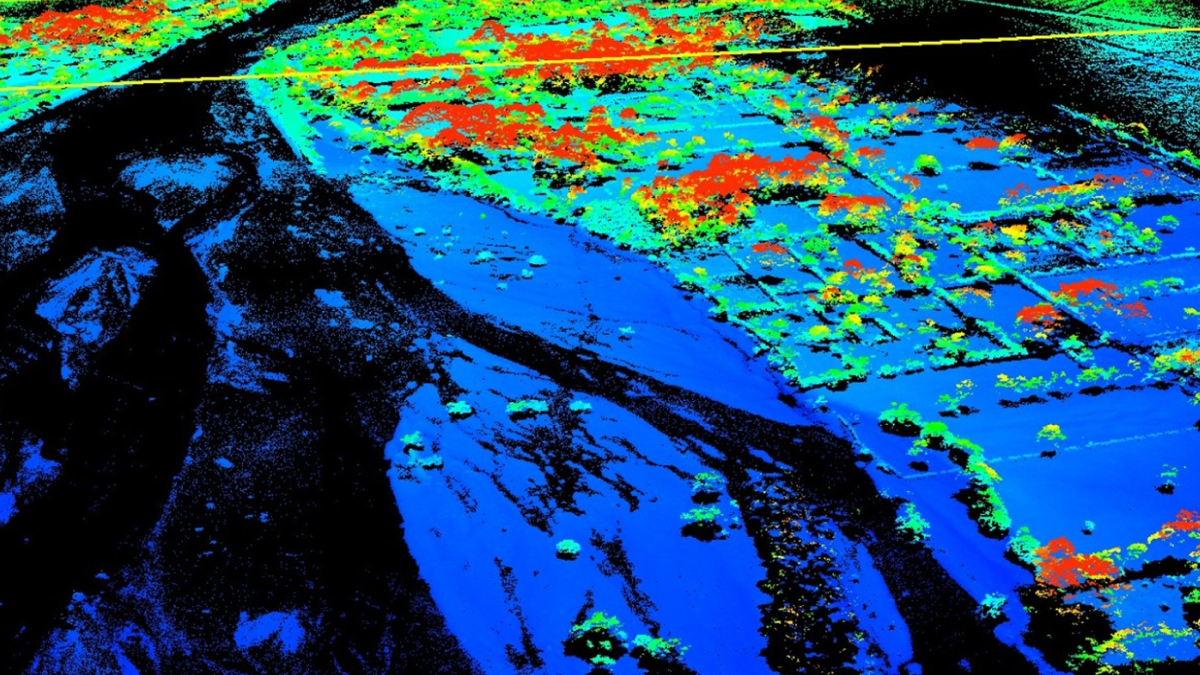
The first technology we looked at, which was the offload autonomous vehicle, relies on LiDAR to navigate its surroundings. This creates a 3D Point Cloud, which is a representation of how the AI system understands the physical world. This 3D Point Cloud needs to be annotated with techniques like object classification. The goal of object classification is to determine the class of each feature, such as a building. For example, you can use it to determine if a building is damaged after a natural disaster.
Polygon annotation may also be necessary here because this is what allows the AI system to detect various objects like trees, plants, and anything else it encounters along the way. In general, polygon annotation is useful for labeling objects that do not neatly fit into 2D or 3D boxes, since it gives the AI system a better understanding of an object’s size.
Finally, we already mentioned in the section about evaluating the extent of the damage that this tool relies on semantic segmentation, but what exactly is that? Semantic segmentation annotation is used by an AI model to learn how to identify individual objects and classes within an image by manually labeling each pixel. It helps an AI model to recognize objects and better understand the context of an image.
Trust Mindy Support With All of your Data Annotation Needs
Mindy Support is a global provider of data annotation services and is trusted by Fortune 500 and GAFAM companies. With more than ten years of experience under our belt and offices and representatives in Cyprus, Poland, Romania, The Netherlands, India, OAE, and Ukraine, Mindy Support’s team now stands strong with 2000+ professionals helping companies with their most advanced data annotation challenges.