Data Annotation for Computer Vision: Everything You Need to Know
For many decades, people dreamed of creating machines with the characteristics of human intelligence, those that can think and act like humans. One of the most fascinating ideas was to give computers the ability to “see” and interpret the world around them. The fiction of yesterday has become the fact of today. Thanks to advancements in artificial intelligence and computational power, computer vision technology has taken a huge leap toward integration in our daily lives.
In this article we will take a closer look at computer vision to understand what it is, how it is used to create AI technologies and the data annotation that is necessary to create it.
What is Computer Vision
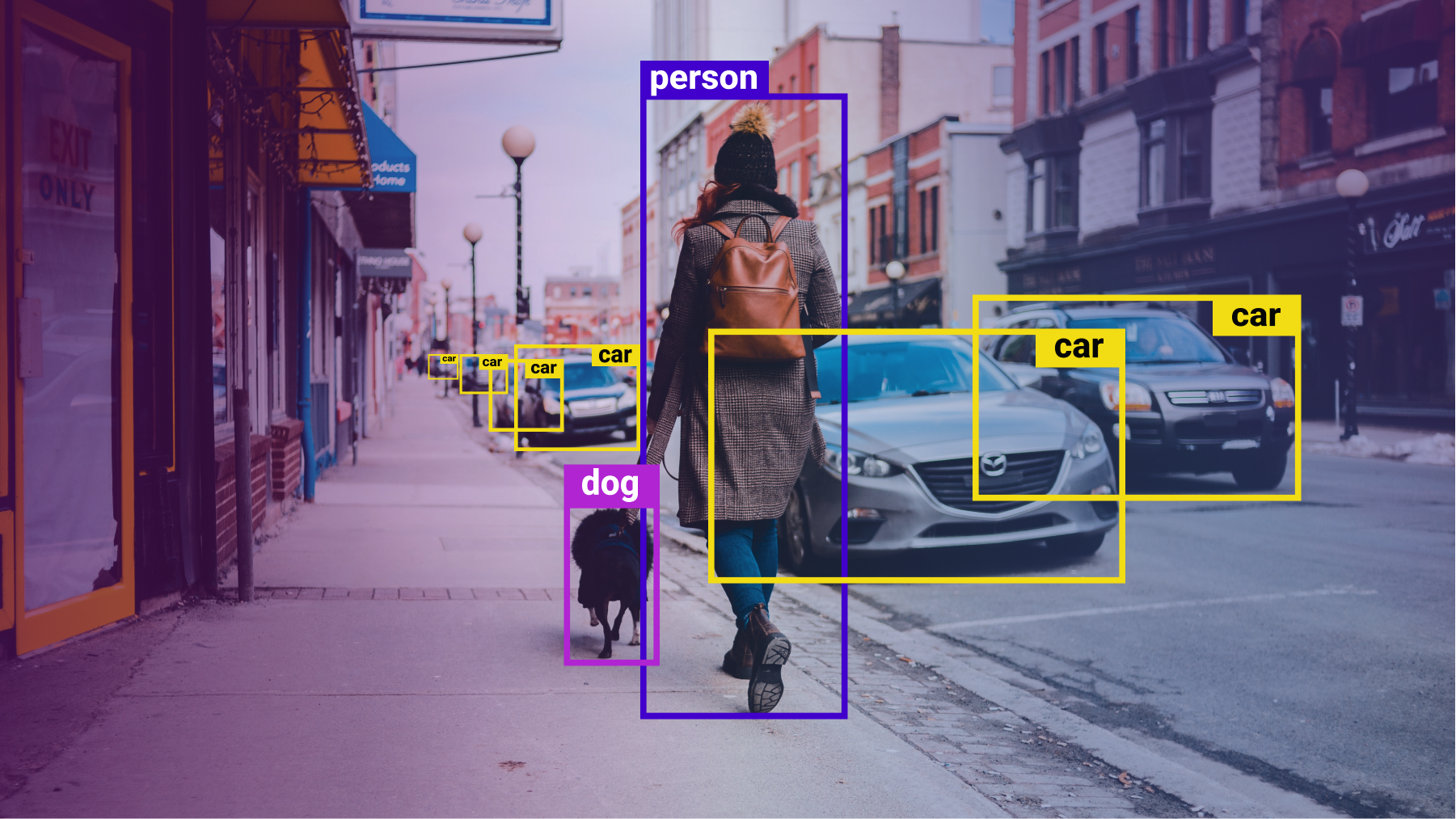
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables computers and systems to derive meaningful information from digital images, videos and other visual inputs — and take actions or make recommendations based on that information. If AI enables computers to think, computer vision enables them to see, observe and understand.
Just like a human can take one look at an object and understand what it is and some of its characteristics, a machine can do the same, if it is trained correctly to do so. You see, humans have an advantage of lifetimes of context to train how to tell objects apart, how far away they are, whether they are moving and whether there is something wrong in an image. Therefore, computer vision performs the same functions, but it does so with data and cameras.
Computer vision systems need to be trained with annotated training datasets, which allow them to recognize objects in the real world. Having said this, there are many types and techniques of data annotation which may be needed, depending on the specifications of the project. In the next section we will go over some of the most common types of data annotation for computer vision.
Image Annotation for Computer Vision
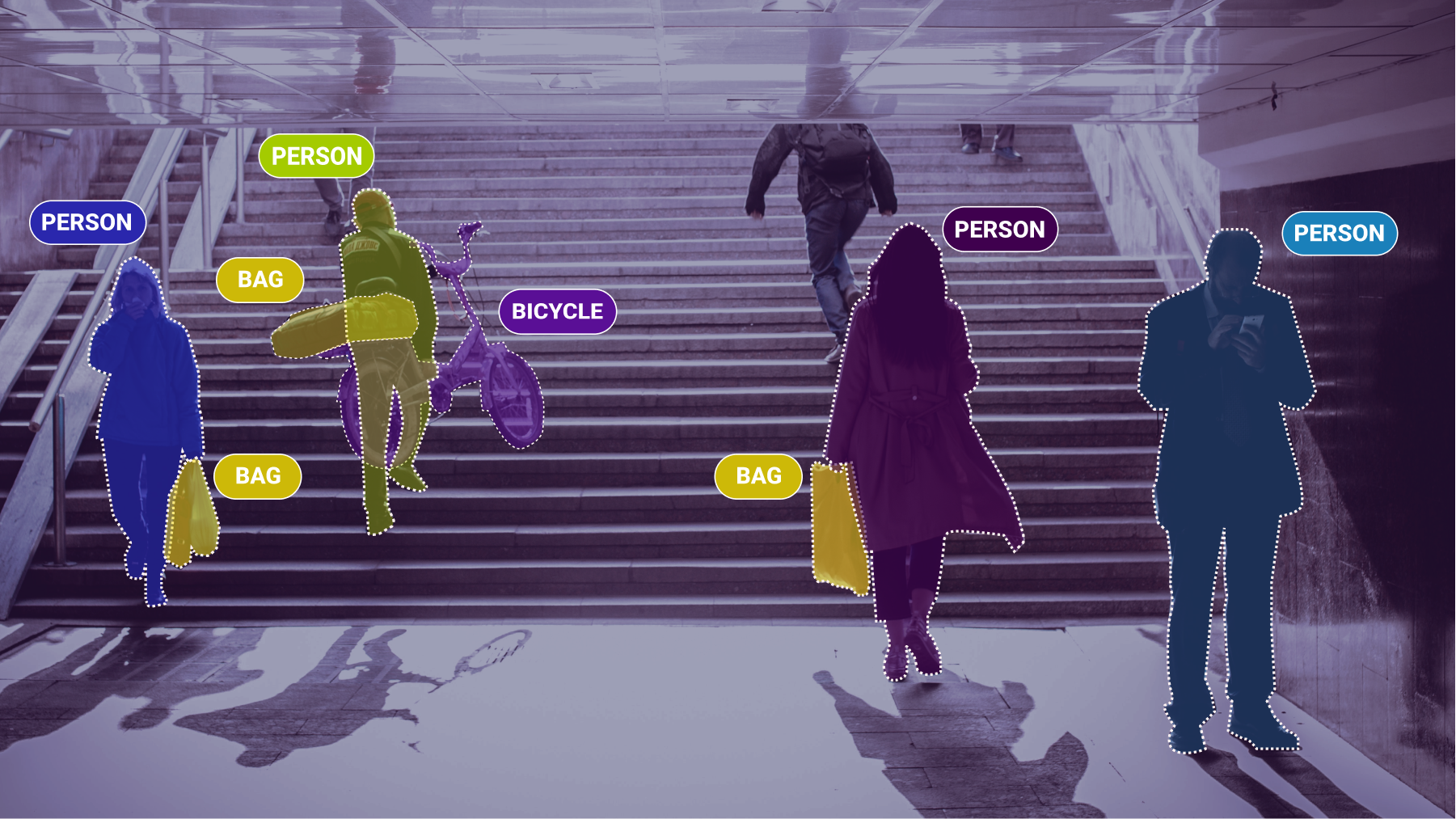

Image annotation is a subset of data annotation where the annotation focuses on still digital images. This work allows the image-specific information to be passed along to the computer vision model being trained.
In some cases, the image annotation process can be automated, which will help move the project along. However, there are also cases where the annotation process will need to be done manually, but the quality of the annotation will be higher. This is a critical aspect of the overall AI project because this is what allows computer vision to understand and process what it sees in the physical world. Now that we got a general overview of image annotation, let’s dive deeper and explore the various types of image annotation.
Types of Image Data Annotation for Computer Vision
While image annotation is necessary to train computer vision systems, image annotation can further be broken down into various types of annotation. Let’s take a look at the different types of image annotation:
- Image classification – This refers to assigning a label or a class to an entire image
- Object recognition/detection – This involves identifying objects in images and videos
- Boundary recognition – Here, salient boundaries are detected and localized between objects in the scene
- Semantic segmentation – A class label to every pixel in the image is assigned
- Instance segmentation – Instances of objects are detected and their boundaries are demarcated
- Panoptic segmentation – An image segmentation task that combines the prediction from both instance and semantic segmentation into a general unified output
Video Annotation for Computer Vision
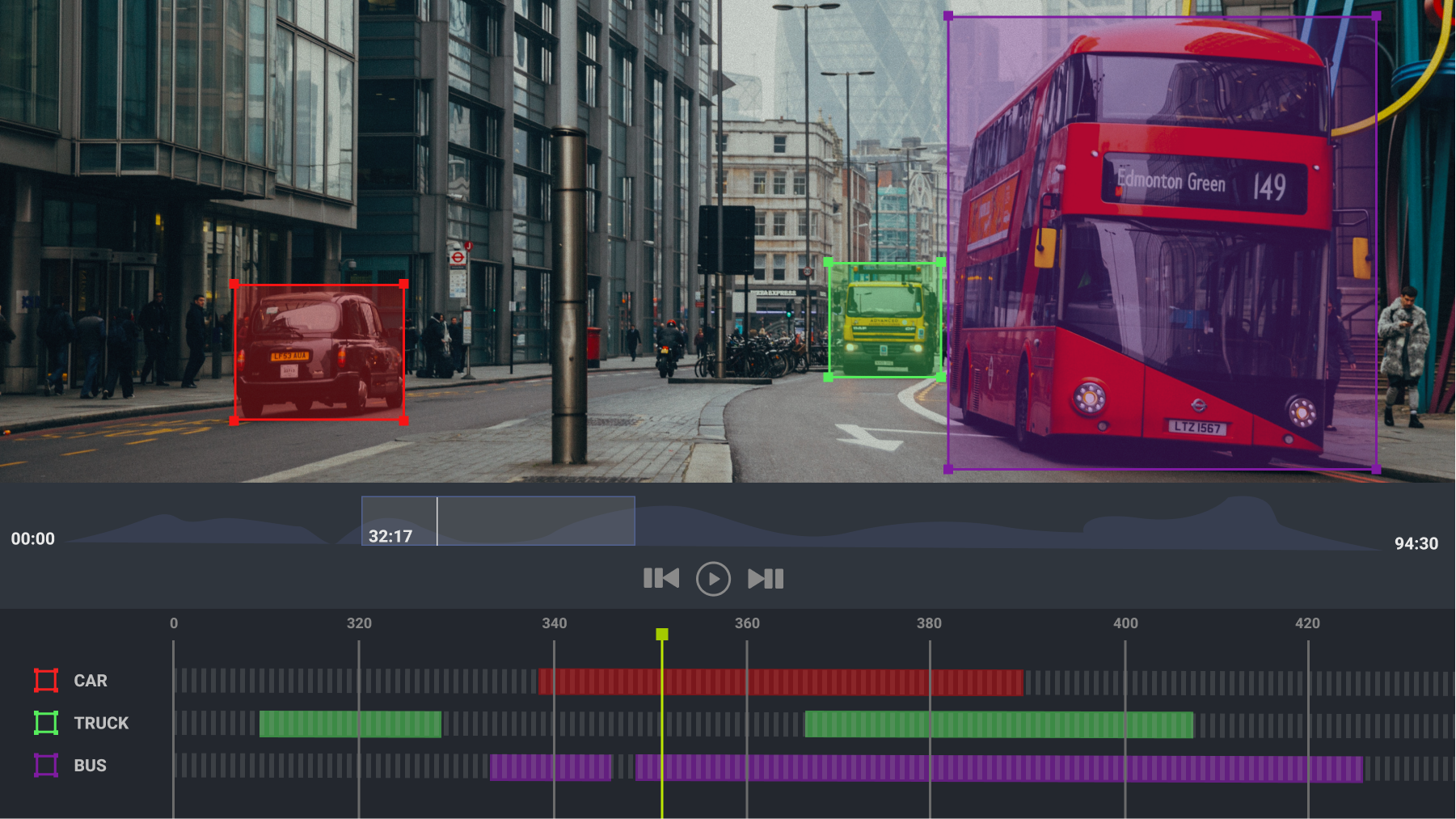
Video annotation is similar to image annotation except it basically deals with moving images. The labels are added to objects in video clips, which trains the AI system to view the world just like a human. Data annotators are responsible for annotating every frame in the video, which is time-consuming since the video can be shot in 30 frames per second (fps) or even 60 fps if it is a high quality video. Therefore, even if you have a video that is only 2 minutes long, but it was shot in 60 fps, that’s already 7,200 frames that need to be annotated.
Types of Video Data Annotation for Computer Vision
Now, let’s take a closer look at the various types of video annotation:
- 3D Cuboid Annotation – is used for an accurate 3D representation of objects. The 3D bounding box method helps label the object’s length, width, and depth when in motion
- Polylines – This type of annotation is mostly used in the automotive area. It helps train computer-based AI tools to detect street lanes for developing high-accuracy autonomous vehicle systems.
- Polygons – Polygon annotation allows all of the object’s exact edges to be annotated, regardless of shape.
- Event Tracking – This involves annotating the video tracks, localizing and labeling events of interest in time. This method is used for detecting all events of interest.
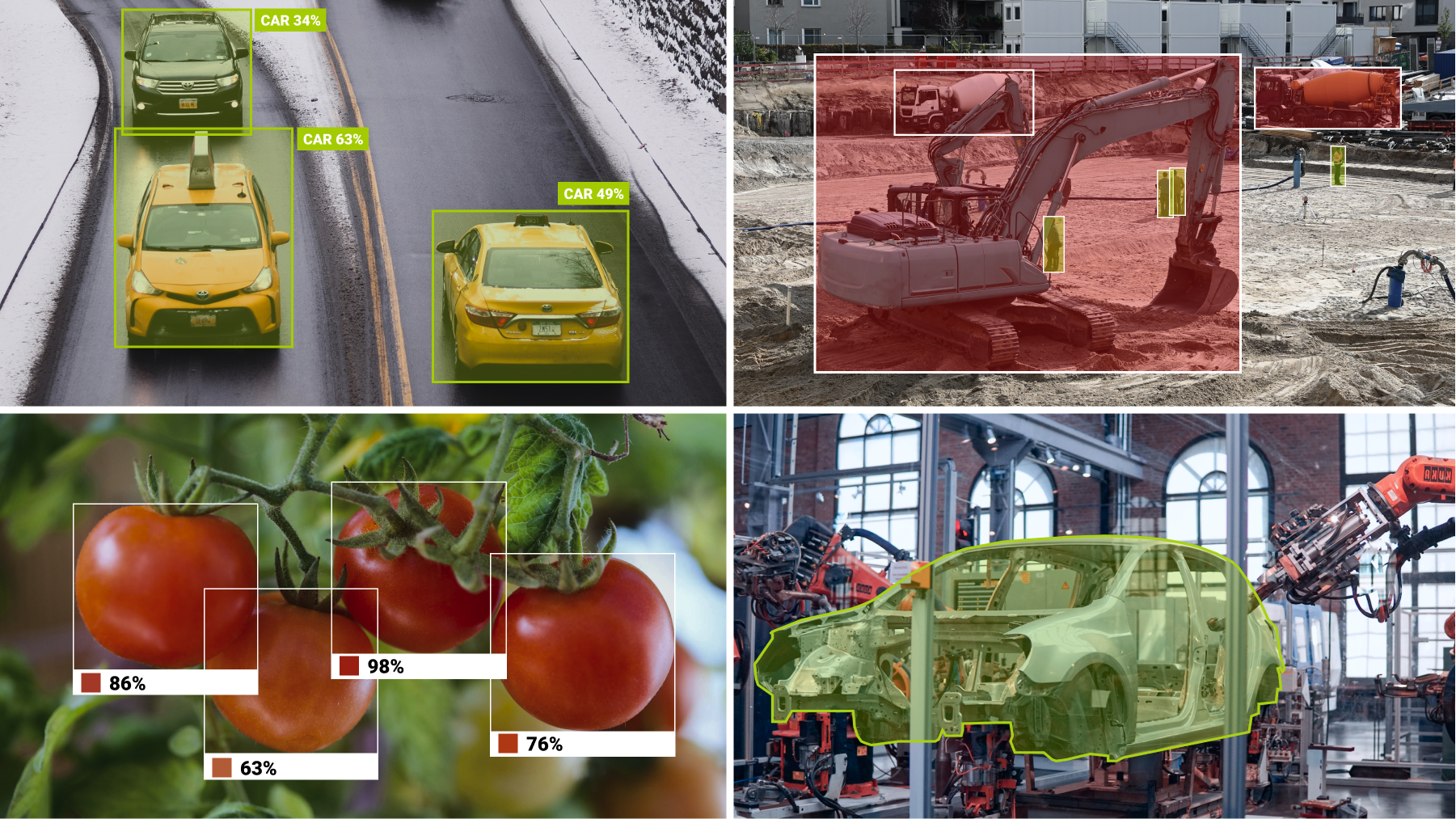
Industries Where Computer Vision is Used Most Often
Computer vision is a rapidly growing technology which is projected to reach $41.11 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 16.0% from 2020 to 2030. The following industries have already started taking advantage of computer vision to provide their customers with greater experiences:
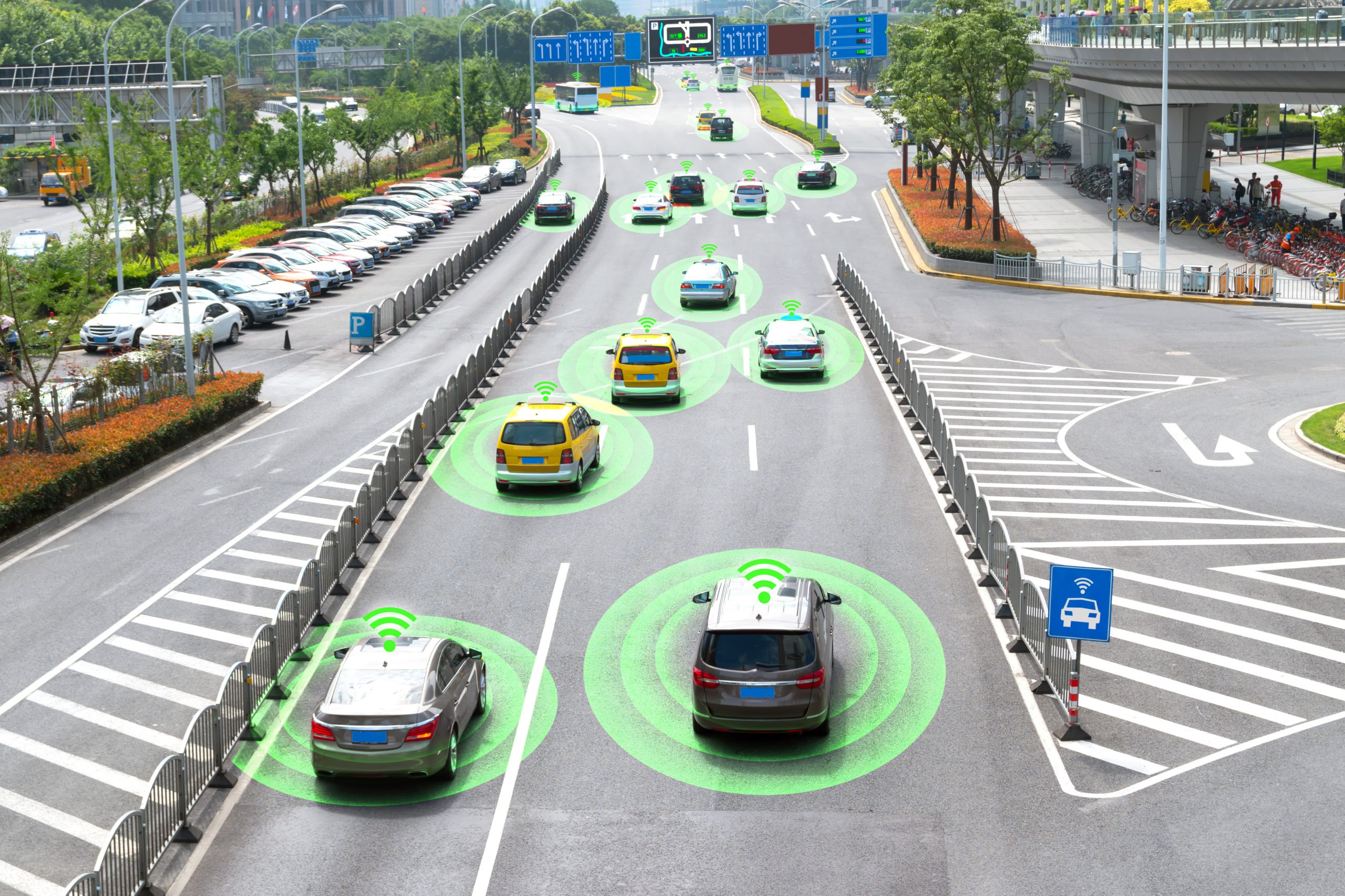
- Automotive – Computer vision is also an integral element of ADAS and autonomous vehicles. For example, the technology can be used to recognize objects around, detect obstacles and pavement defects to improve driver’s awareness of the road, increasing his safety, and allowing autonomous vehicles to navigate the road.
- Agriculture – Computer vision is widely used to monitor field condition, detect weeds, analyze health of the crops, and monitor its growth. Farmers use computer vision in real time to manage livestock, detect abnormal behavior, and monitor health of the animals.
- Manufacturing and Robotics – The technology allows the industrial robots to ‘see’ their surroundings and perform various tasks of the factories. Computer vision also can be used to improve the industrial workplace safety: for example, track if all workers wear helmets or keep a secure distance to the dangerous objects.
- Construction – Companies can use computer vision-powered cameras to automatically detect and classify construction zones in order to help improve safety and security on the construction site. Computer vision is already being used to monitor construction sites to identify potentially hazardous conditions and as well as the pace of construction.
Computer Vision Use Case: Enhancing the Accuracy of ADAS Technology to Improve Driver’s Road Awareness
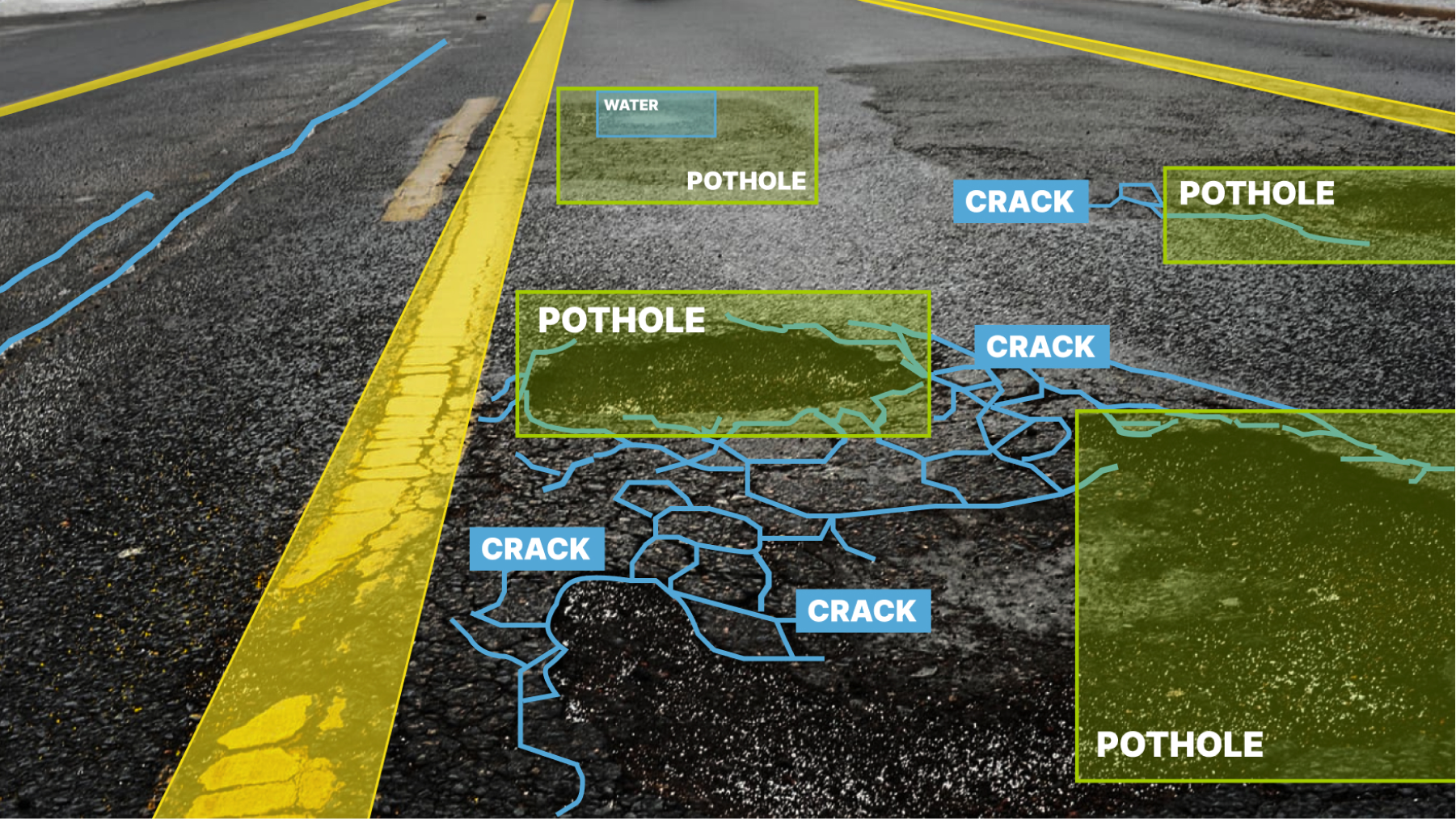
One of the main applications of computer vision is in the automotive sector, specifically with autonomous vehicles. The reason for this is that if we are ever going to get to Level 5 automation, the car needs to see and understand everything on the road just like a human. While we are not at Level 5 yet, vehicles today have some AI capabilities in the form of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). In fact, at Mindy Support, we recently worked on an interesting project for a client who was working on an ADAS system that could accurately detect road markings and various obstacles on the road. This included things like potholes, water, delineator markings and many other things.
We annotated a training dataset of 60,000 images with semantic segmentation and polyline annotation with an accuracy rate of 95%+. High attention to detail was absolutely critical since some of the cracks on the road were very small, yet they were very important to annotate for the overall accuracy of the model. Learn more about the work we did in our case study.
Computer Vision Use Case: Streamlining Car Damage Detection
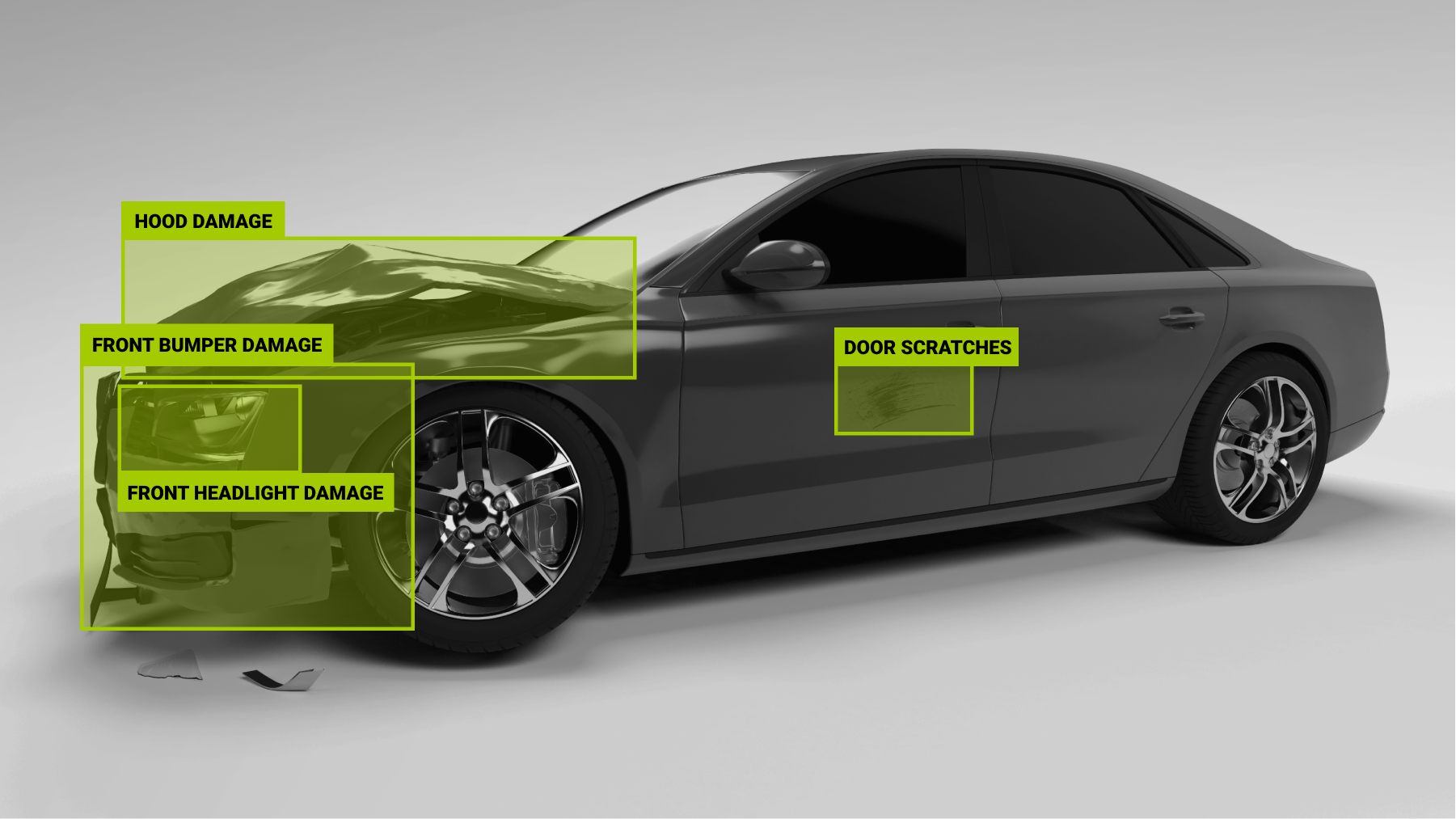
Another forward-thinking project we worked on was an AI solution that could not only detect damage caused to cars but also provided the clients with additional services such as submitting a claim, appraising the damage, predicting the type of repair required, and a lot of other useful information. We annotated 36,000 images with 2D bounding boxes. Some images contained many objects for annotation of different types, and annotators needed to be extra careful in object recognition and classifying. Learn more about the solutions we provided to the client in our case study.
Trust Mindy Support With All of Your Data Annotation Needs
Mindy Support is a global provider of data annotation services, trusted by Fortune 500 and GAFAM companies, as well as innovative startups. With 10 years of experience under our belt and offices and representatives in Cyprus, Poland, Romania, The Netherlands, India, OAE, and Ukraine, Mindy Support’s team now stands strong with 2000+ professionals helping companies with their most advanced data annotation challenges.