AI Tractors Offer Farmers an Abundance of Benefits
Imagine a tractor that not only thinks, but also sees. A tractor that’s always ready to work, no matter how early or how late. A tractor that lets you and your operators tackle other jobs while it does its job by itself. Thanks to new developments in AI, these tools are now available for farmers to use to increase their crop growth, reduce manual tasks, and improve overall productivity. In this article, we will take a look at AI tractors, how they can make the lives of farmers a lot easier, and the data annotation needed to create them.
How Can an AI Tractor Navigate Its Surroundings?

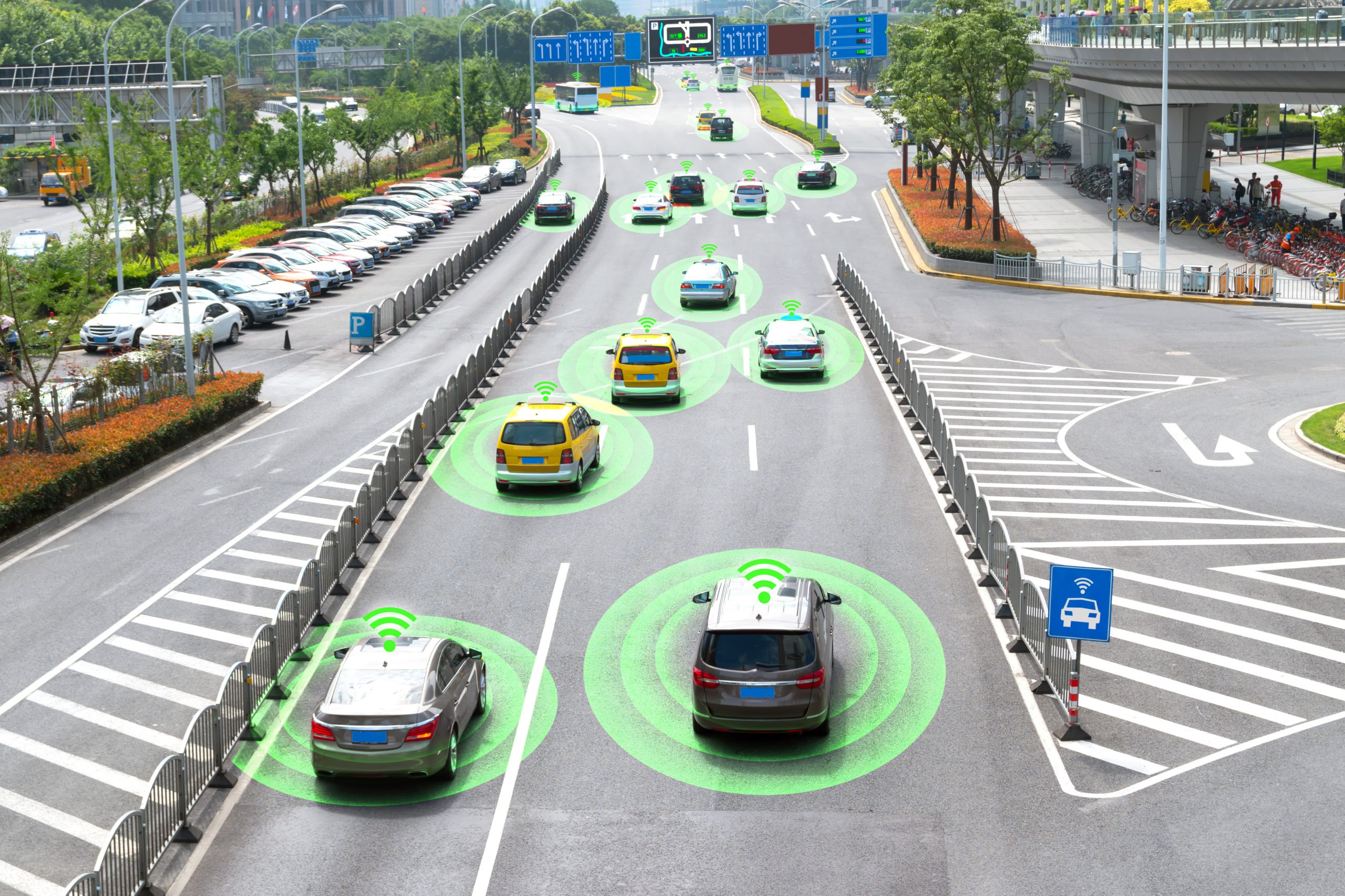
AI-powered tractors rely on computer vision cameras to perceive their environment and navigate. When given a route and coordinates, it can get to a field on its own. Once there, it can plow the ground or scatter seeds without further instructions while dodging obstacles. Using a smartphone app, a farmer can give the machine fresh instructions. Some tractors already run on their own, but only in specific circumstances. For instance, they can only follow GPS-defined routes without being able to avoid obstacles. Others have a limited degree of autonomy, but still need a farmer to operate the steering wheel.
What Benefits Can AI Tractors Offer Farmers?
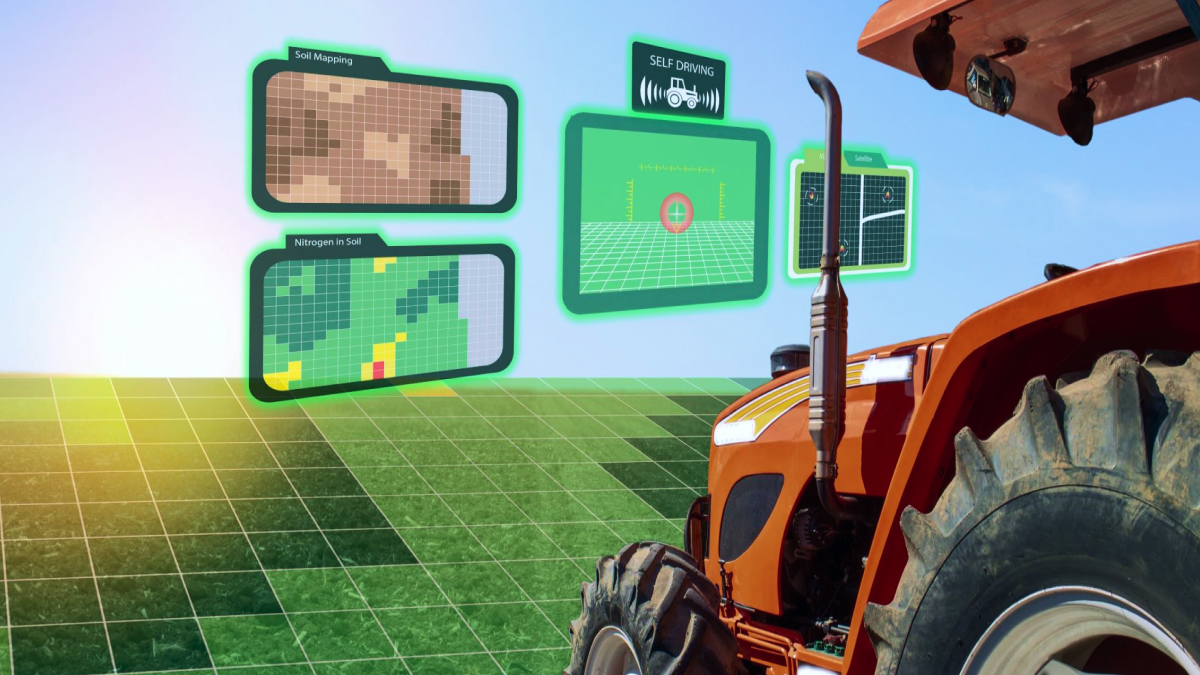

The AI tractors can help farmers increase their crop yields by collecting and analyzing data from the fields. For example, AI platforms combined with tractors use sophisticated computer vision, data science, and deep learning algorithms to enable farmers to make informed decisions. These platforms can keep an eye on fields and spot early signs of uneven emergence, weed growth, nutrient deficiency, disease or insect infestations, water damage, and equipment problems. They use deep learning techniques to “teach” the program how each issue appears differently from crop to crop. This is an extremely complicated operation that needs precise data collection made up of millions of symptoms.
Additional benefits of AI tractors include:
- Increased productivity – The first and most obvious benefit is the considerable increase in productivity. The addition of autonomous tractors to a farm’s fleet boosts farm productivity as precision agriculture becomes the standard. They are able to operate around the clock, which speeds up farm activities and raises farm productivity. Dairy farms, which operate 24 hours a day, find this to be a particularly useful feature because feeding cows at all hours of the day and night can boost milk production. Although the initial cost of an autonomous tractor may be higher (though this cost may be reduced if the tractor is eligible for EV tax credits like California’s CORE program), the ROI increases over time.
- Help deal with labor shortages – Farmers struggle to fill positions due to a shortage of farmworkers. This is particularly true for tractor operators, who are often criticized for doing dangerous, unpleasant, and boring jobs. One operator can oversee several autonomous tractors at once, thanks to them. Operations can be completed promptly. When autonomy and electrification are combined, a tractor will need less maintenance and downtime than a traditional diesel tractor. Farmers are likely to have a tractor ready to go for operations that need to be completed quickly, in addition to empowering their personnel to accomplish more. Helping tractor operators gain expertise in a digital setting has further advantages. It develops into a transferrable ability that aids in their job advancement.
- Improve sustainability – When autonomous tractors are also electric tractors, they significantly contribute to the cost parity that organic and sustainable farming methods eventually reach with traditional farming methods. Their precise operations guarantee the best use of resources, minimizing waste and lowering the impact of farming on the environment. In contrast, electrification makes it possible for farmers to use organic farming’s essential renewable farming techniques. As a result, producers may satisfy the public’s growing demand for sustainability while also gaining from improved production, efficiency, and environmentally sound farming practices.
What Types of Data Annotation are Needed to Create These Technologies?
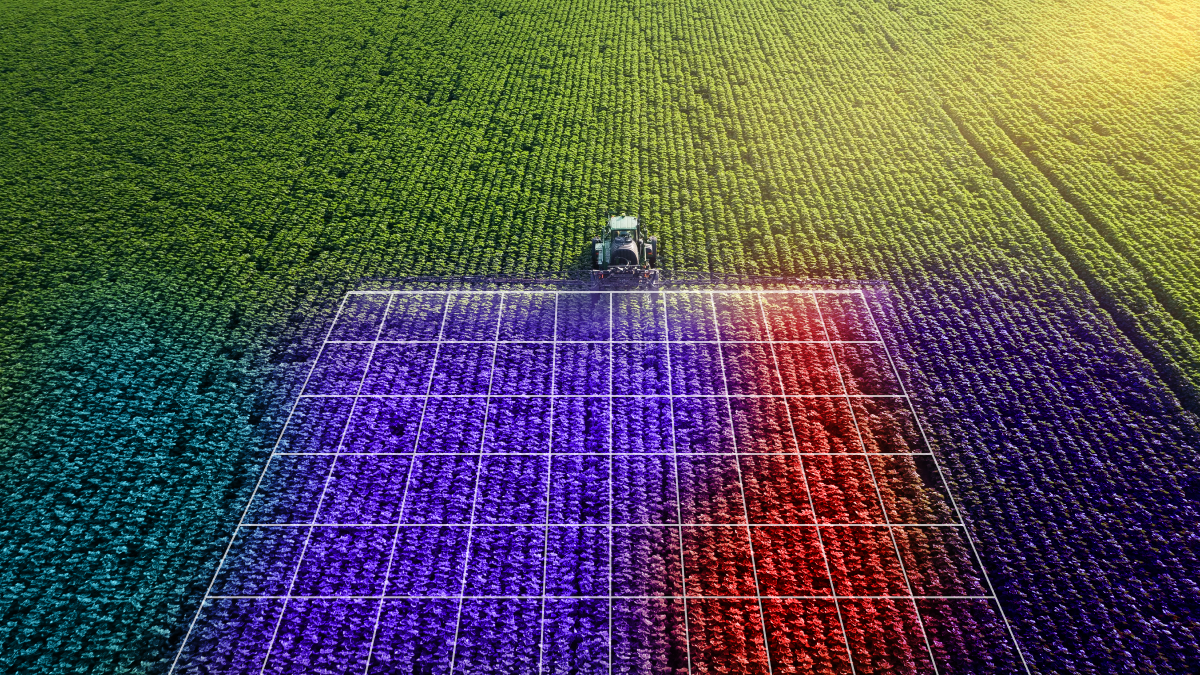

AI tractors rely on computer vision to help them navigate the physical world. This means that data annotation techniques like instance segmentation support the system’s learning to recognize objects, locate each one in the frame, and estimate its precise pixel count. These models can be helpful if you require more accuracy and more exact pixel estimations for object interactions. To identify the distinctive pixels that correspond to an item in these models, polygon labels are required. An area where AI-powered solutions can excel is in the manual labeling of polygons, which is known to be arduous and time-consuming.
Bounding box annotation will also be necessary, which involves drawing a bounding box around an object in an image — such as various types of crops— and is one of several ways to annotate and label objects. Any object can have a rectangular box drawn around it using bounding boxes, after which the object can have a label applied. A bounding box serves as a visual reference for machine learning models that have been trained to recognize and detect objects in images and to specify the object’s spatial extent. In applications like object detection, where the objective is to determine the existence and placement of particular items within an image, bounding boxes are frequently utilized.
Trust Mindy Support With All of Your Data Annotation Needs
Mindy Support is a global provider of data annotation services and is trusted by Fortune 500 and GAFAM companies. With more than ten years of experience under our belt and offices and representatives in Cyprus, Poland, Romania, The Netherlands, India, OAE, and Ukraine, Mindy Support’s team now stands strong with 2000+ professionals helping companies with their most advanced data annotation challenges.