AI Buses Can Make Transportation More Accessible
The concept of an autonomous bus seemed like science fiction decades ago. Though most people never thought that we would live in a world where cars could drive themselves, it seems possible that this day may come sooner than we had anticipated.
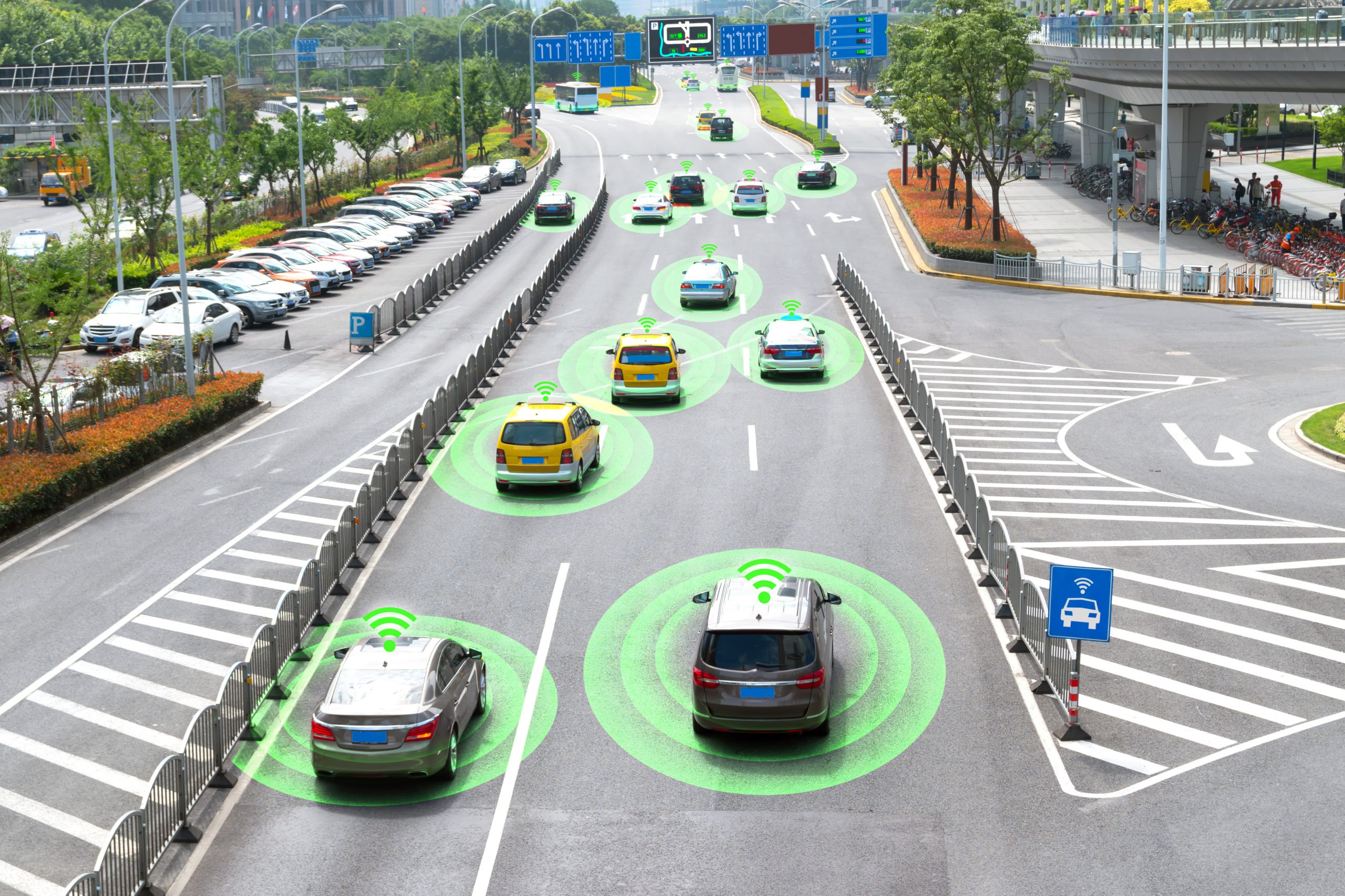
Major technological advancements in recent years have made it possible for cars and buses to drive themselves. Passengers are getting the chance to travel in whole new ways thanks to innovators, and a select group of them are driving this trend. The development and use of autonomous buses are expected to stimulate the public transportation sector in large cities, as usage of the mode has been continuously declining.
In this article, we will take a look at self-driving buses, how they are improving accessibility for passengers, and the data annotation needed to create them.
Self-driving buses are Tested Out in the UK
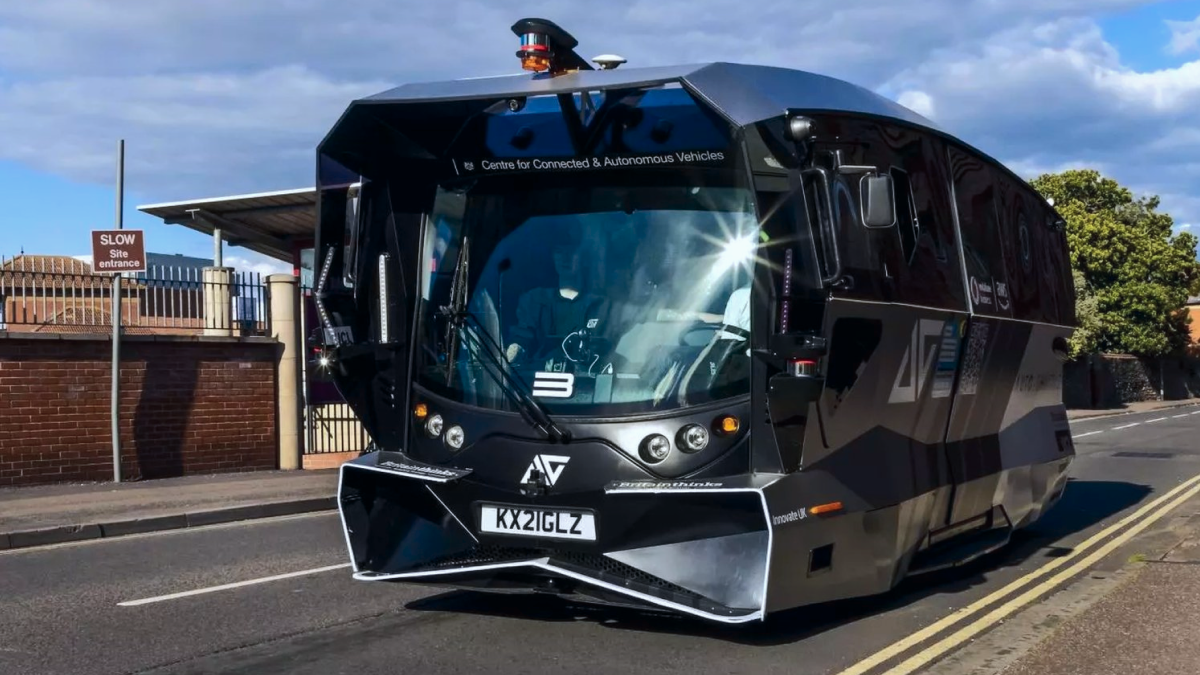

This week, a brand-new autonomous vehicle in Central Milton Keynes is prepared to pick up passengers. This week saw the introduction of the fully accessible electric shuttle, which can accommodate up to 15 passengers. It makes a loop between Santander’s new UK headquarters at Unity Place, center MK, the Theatre District, and Station Square. Milton Keynes was selected to trial the new shuttle as part of a Europe-wide research project that is the longest and most geographically complex of its kind. The LivingLAPT project is funded by EIT Urban Mobility and led by University College London (UCL).
The autonomous shuttle creates a 360-degree picture surrounding the vehicle and navigates public highways securely using five LIDAR sensors and seven cameras. There’s an operator on board who can take over at any moment. The trial comes after comparable, fruitful trials that were conducted in 2022 in Helmond, Hasselt, Kongsberg, and Ricany and in 2023 in Prague and Brno, Czech Republic.
How Do AI Buses Improve Accessibility to Transportation?
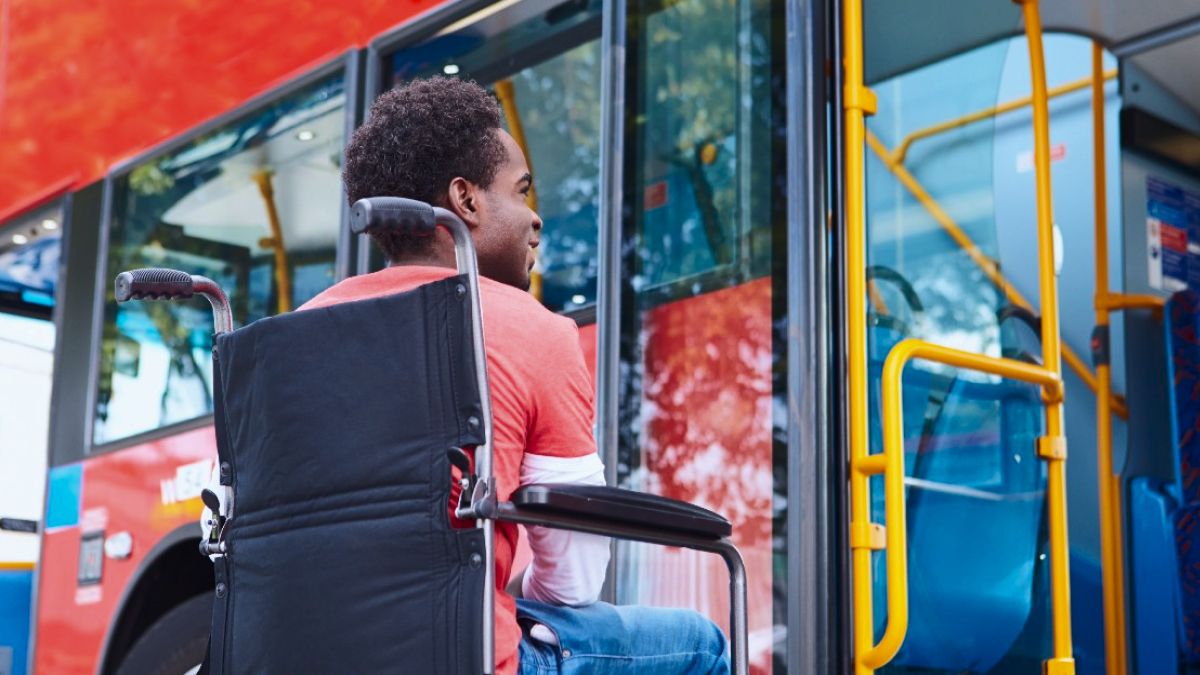

Scheduling and route planning optimization is one of the most useful uses of AI in public transportation. AI systems can forecast demand for certain routes by evaluating past data, which enables transit authorities to modify timetables and resources appropriately. As a result, the customer experience is enhanced by more precise and timely arrival time information, improved traffic management, and less crowding.
In addition to this, for travelers with disabilities, AI-driven solutions can greatly increase the accessibility of public transit. Transit agencies may enhance passenger communication and transit station way finding by integrating AI-powered technologies like computer vision, voice recognition, and natural language processing. These improvements provide improved access to mass transit and a more welcoming atmosphere for all passengers, irrespective of their physical capabilities.
What Types of Data Annotation are Needed to Create AI Buses?
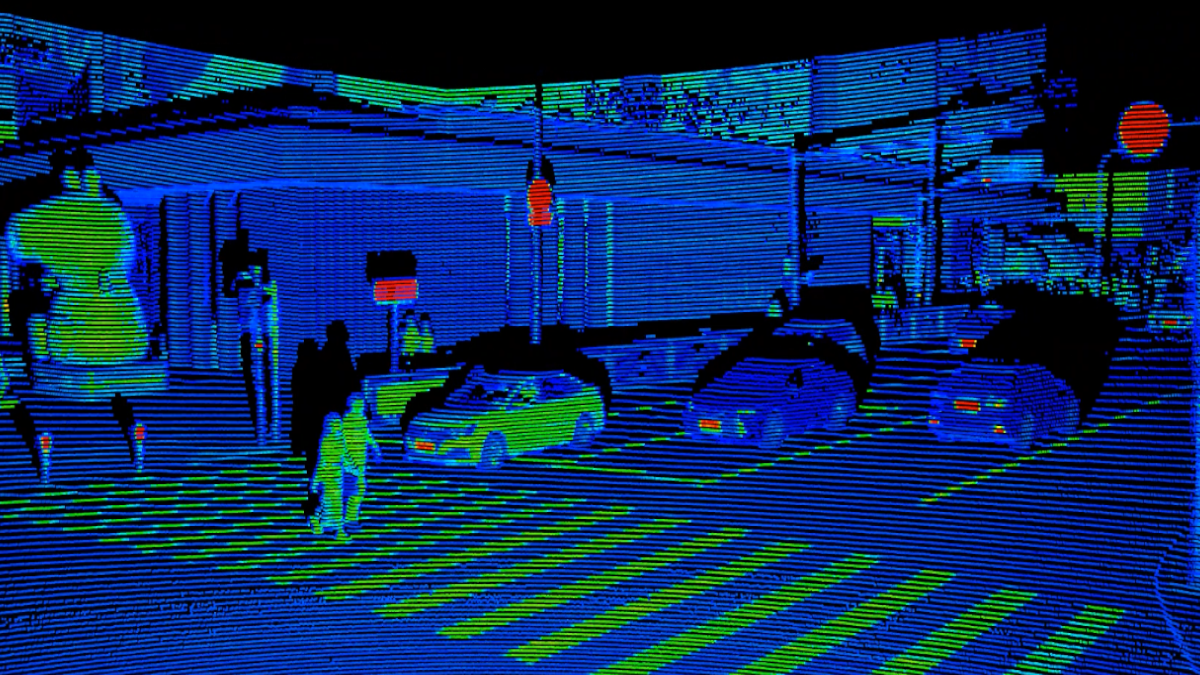
One of the main tools AI technologies rely on to navigate the physical world is LiDAR, which sends out pulses of light that bounce off objects and return to the LiDAR. This creates a 3D Point Cloud, which is a digital representation of how the AI system views its surrounding environment. This 3D Point Cloud needs to be annotated with methods like polyline annotation, which aids in the detection of street lanes across highways and cities by autonomous cars. Semantic segmentation will also be necessary, which is a deep learning system that assigns each pixel in a picture a name or category. It is employed to identify a group of pixels that make up different categories. An autonomous car must be able to recognize, for instance, other cars, pedestrians, traffic signs, pavement, and other elements of the route.
Additional data sources like images are often used to train AI vehicles. These images often need to be annotated with 2D bounding boxes, which is the most widely used kind of data annotation. To indicate that there is an object visible in the surroundings, a square or rectangular line is drawn around the object of interest in 2D image annotation. 3D bounding boxes can also be used to add an extra dimension to the object’s size. However, if an object does not neatly fit into the bounding box, it would be best to use polygon annotation.
Trust Mindy Support With All of Your Data Annotation Needs
Mindy Support is a global provider of data annotation services and is trusted by Fortune 500 and GAFAM companies. With more than ten years of experience under our belt and offices and representatives in Cyprus, Poland, Romania, The Netherlands, India, OAE, and Ukraine, Mindy Support’s team now stands strong with 2000+ professionals helping companies with their most advanced data annotation challenges.